Page 284 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 284
250 Handbook of gold exploration and evaluation
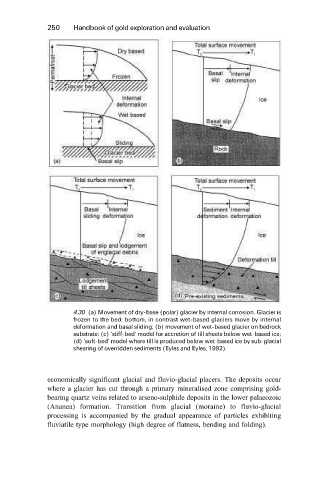
4.30 (a) Movement of dry-base (polar) glacier by internal corrosion. Glacier is
frozen to the bed: bottom, in contrast wet-based glaciers move by internal
deformation and basal sliding; (b) movement of wet-based glacier on bedrock
substrate; (c) `stiff-bed' model for accretion of till sheets below wet-based ice;
(d) `soft-bed' model where till is produced below wet-based ice by sub-glacial
shearing of overridden sediments (Eyles and Eyles, 1992).
economically significant glacial and fluvio-glacial placers. The deposits occur
where a glacier has cut through a primary mineralised zone comprising gold-
bearing quartz veins related to arseno-sulphide deposits in the lower palaeozoic
(Ananea) formation. Transition from glacial (moraine) to fluvio-glacial
processing is accompanied by the gradual appearance of particles exhibiting
fluviatile type morphology (high degree of flatness, bending and folding).