Page 325 - Handbook of Lasers
P. 325
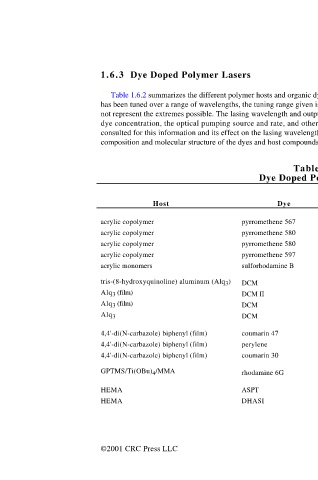
1.6.3 Dye Doped Polymer Lasers
Table 1.6.2 summarizes the different polymer hosts and organic dye dopants that have been used to demonstrate laser action. If the laser
has been tuned over a range of wavelengths, the tuning range given is that for the experimental configuration and conditions used and may
not represent the extremes possible. The lasing wavelength and output of dye lasers depend on the characteristics of the optical cavity, the
dye concentration, the optical pumping source and rate, and other operating conditions. The original references should therefore be
consulted for this information and its effect on the lasing wavelength. The references should also be consulted for details of the chemical
composition and molecular structure of the dyes and host compounds.
Table 1.6.2
Dye Doped Polymer Lasers
Laser
wavelength Pump source
Host Dye (nm) (wavelength – nm) Ref.
acrylic copolymer pyrromethene 567 564 Nd:YAG laser (532) 1
acrylic copolymer pyrromethene 580 570 Nd:YAG laser (532) 2
acrylic copolymer pyrromethene 580 571 Nd:YAG laser (532) 3
acrylic copolymer pyrromethene 597 587 Nd:YAG laser (532) 1, 4
acrylic monomers sulforhodamine B ~600 5
tris-(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum (Alq 3 ) DCM 589–635 (a) N 2 laser (337) - ET 6
Alq 3 (film) DCM II 613 N 2 laser (337) - ET 9
Alq 3 (film) DCM 645 N 2 laser (337) - ET 7
Alq 3 DCM ~655 N 2 laser (337) - ET 8
4,4'-di(N-carbazole) biphenyl (film) coumarin 47 460 N 2 laser (337) - ET 10
4,4'-di(N-carbazole) biphenyl (film) perylene 485 N 2 laser (337) - ET 10
4,4'-di(N-carbazole) biphenyl (film) coumarin 30 510 N 2 laser (337) - ET 10
GPTMS/Ti(OBu) 4 /MMA rhodamine 6G 564–587 Nd:YAG laser (532) 58
HEMA ASPT ~600 Nd:YAG laser (1064) - TP 11
HEMA DHASI ~606 Nd:YAG laser (1064) - TP 12
©2001 CRC Press LLC