Page 33 - Handbook of Materials Failure Analysis
P. 33
26 CHAPTER 2 Failure analysis in chemical industries
3.2.4 Review of the Process ...............................................................41
3.2.5 Testing Results and Findings .....................................................42
3.2.6 Conclusion ...............................................................................43
3.2.7 Recommendations ....................................................................44
Acknowledgment ......................................................................................................45
References ..............................................................................................................46
1 INTRODUCTION
The engineering materials are utilized into useful products which are molded and
designed to serve mankind for some specific purpose to fulfill needs. The job starts
from design engineer who conceives idea, makes plan, and manufactures product to
meet intended requirements for some specific service life. In other words, efficient per-
formance of a product depends on design, manufacturing, operation under predefined
conditions, and periodic maintenance according to specifications. All these aspects
determine the reliability and durability of product under set criteria. Any fault, short-
coming, or flaw at any stage could lead to failure. It may be precluded that the failure of
a component at any stage of its lifecycle could happen which may result in decrease of
process efficiency, unintended shutdowns, time wastage, loss of money, and in most
sever scenario loss of human lives [1,2]. The deviation from the conceptual design,
prescribed manufacturing steps, and non-recommended operational conditions could
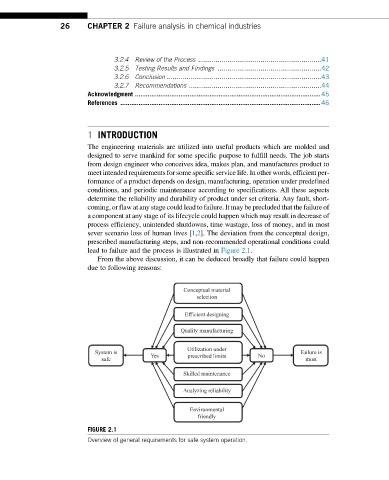
lead to failure and the process is illustrated in Figure 2.1.
From the above discussion, it can be deduced broadly that failure could happen
due to following reasons:
Conceptual material
selection
Efficient designing
Quality manufacturing
Utilization under
System is Failure is
Yes prescribed limits No
safe must
Skilled maintenance
Analyzing reliability
Environmental
friendly
FIGURE 2.1
Overview of general requirements for safe system operation.