Page 89 - Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing Principles and Practices
P. 89
with respect to unknowns .
Efficient saturation-point calculation algorithms can be found in the reference book by Michelsen
and Mollerup (2007).
2.2.5.7. Calculation Principle of a PT Flash
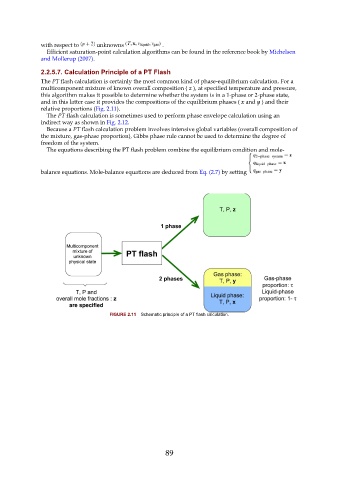
The PT flash calculation is certainly the most common kind of phase-equilibrium calculation. For a
multicomponent mixture of known overall composition ( z ), at specified temperature and pressure,
this algorithm makes it possible to determine whether the system is in a 1-phase or 2-phase state,
and in this latter case it provides the compositions of the equilibrium phases ( x and y ) and their
relative proportions (Fig. 2.11).
The PT flash calculation is sometimes used to perform phase envelope calculation using an
indirect way as shown in Fig. 2.12.
Because a PT flash calculation problem involves intensive global variables (overall composition of
the mixture, gas-phase proportion), Gibbs phase rule cannot be used to determine the degree of
freedom of the system.
The equations describing the PT flash problem combine the equilibrium condition and mole-
balance equations. Mole-balance equations are deduced from Eq. (2.7) by setting
FIGURE 2.11 Schematic principle of a PT flash calculation.
89