Page 112 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 112
THERMOPLASTICS
2.52 CHAPTER 2
369
PES finds application in aircraft interior parts due to its low smoke emission. Elec-
370
trical applications include switches, integrated circuit carriers, and battery parts. The
high-temperature oil and gas resistance allow polyether sulfone to be used in the automo-
tive markets for water pumps, fuse housings, and car heater fans. The ability of PES to en-
dure repeated sterilization allows PES to be used in a variety of medical applications, such
as parts for centrifuges and root canal drills. Other applications include membranes for
kidney dialysis, chemical separation, and desalination. Consumer uses include cooking
equipment and lighting fittings. PES can also be vacuum metallized for a high-gloss mir-
ror finish.
2.2.27.3 Polysulfone (PSU). Polysulfone is a transparent thermoplastic prepared from
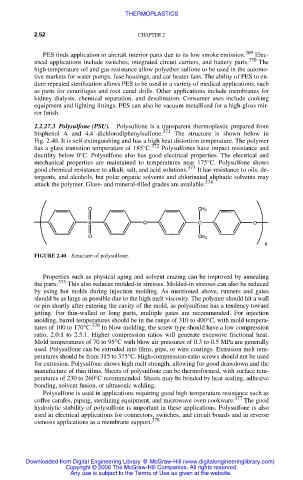
bisphenol A and 4,4´-dichlorodiphenylsulfone. 371 The structure is shown below in
Fig. 2.40. It is self-extinguishing and has a high heat distortion temperature. The polymer
has a glass transition temperature of 185°C. 372 Polysulfones have impact resistance and
ductility below 0°C. Polysulfone also has good electrical properties. The electrical and
mechanical properties are maintained to temperatures near 175°C. Polysulfone shows
good chemical resistance to alkali, salt, and acid solutions. 373 It has resistance to oils, de-
tergents, and alcohols, but polar organic solvents and chlorinated aliphatic solvents may
attack the polymer. Glass- and mineral-filled grades are available. 374
FIGURE 2.40 Structure of polysulfone.
Properties such as physical aging and solvent crazing can be improved by annealing
the parts. 375 This also reduces molded-in stresses. Molded-in stresses can also be reduced
by using hot molds during injection molding. As mentioned above, runners and gates
should be as large as possible due to the high melt viscosity. The polymer should hit a wall
or pin shortly after entering the cavity of the mold, as polysulfone has a tendency toward
jetting. For thin-walled or long parts, multiple gates are recommended. For injection
molding, barrel temperatures should be in the range of 310 to 400°C, with mold tempera-
tures of 100 to 170°C. 376 In blow molding, the screw type should have a low compression
ratio, 2.0:1 to 2.5:1. Higher compression ratios will generate excessive frictional heat.
Mold temperatures of 70 to 95°C with blow air pressures of 0.3 to 0.5 MPa are generally
used. Polysulfone can be extruded into films, pipe, or wire coatings. Extrusion melt tem-
peratures should be from 315 to 375°C. High-compression-ratio screws should not be used
for extrusion. Polysulfone shows high melt strength, allowing for good drawdown and the
manufacture of thin films. Sheets of polysulfone can be thermoformed, with surface tem-
peratures of 230 to 260°C recommended. Sheets may be bonded by heat sealing, adhesive
bonding, solvent fusion, or ultrasonic welding.
Polysulfone is used in applications requiring good high-temperature resistance such as
377
coffee carafes, piping, sterilizing equipment, and microwave oven cookware. The good
hydrolytic stability of polysulfone is important in these applications. Polysulfone is also
used in electrical applications for connectors, switches, and circuit boards and in reverse
378
osmosis applications as a membrane support.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.