Page 195 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 195
THERMOSETS
THERMOSETS 3.65
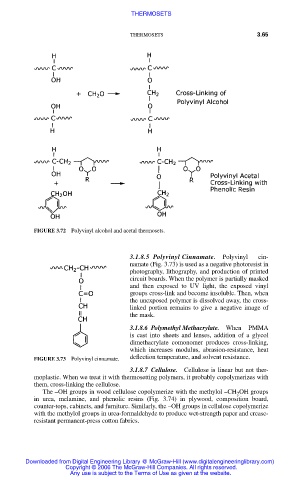
FIGURE 3.72 Polyvinyl alcohol and acetal thermosets.
3.1.8.5 Polyvinyl Cinnamate. Polyvinyl cin-
namate (Fig. 3.73) is used as a negative photoresist in
photography, lithography, and production of printed
circuit boards. When the polymer is partially masked
and then exposed to UV light, the exposed vinyl
groups cross-link and become insoluble. Then, when
the unexposed polymer is dissolved away, the cross-
linked portion remains to give a negative image of
the mask.
3.1.8.6 Polymethyl Methacrylate. When PMMA
is cast into sheets and lenses, addition of a glycol
dimethacrylate comonomer produces cross-linking,
which increases modulus, abrasion-resistance, heat
FIGURE 3.73 Polyvinyl cinnamate. deflection temperature, and solvent resistance.
3.1.8.7 Cellulose. Cellulose is linear but not ther-
moplastic. When we treat it with thermosetting polymers, it probably copolymerizes with
them, cross-linking the cellulose.
The –OH groups in wood cellulose copolymerize with the methylol –CH OH groups
2
in urea, melamine, and phenolic resins (Fig. 3.74) in plywood, composition board,
counter-tops, cabinets, and furniture. Similarly, the –OH groups in cellulose copolymerize
with the methylol groups in urea-formaldehyde to produce wet-strength paper and crease-
resistant permanent-press cotton fabrics.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.