Page 219 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 219
ELASTOMERS
ELASTOMERS 4.11
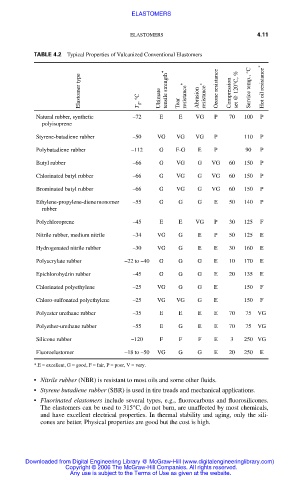
TABLE 4.2 Typical Properties of Vulcanized Conventional Elastomers
Elastomer type T g , °C Ultimate tensile strength * Tear resistance * Abrasion * resistance Ozone resistance Compression set @ 120°C, % Service temp., °C Hot oil resistance *
Natural rubber, synthetic –72 E E VG P 70 100 P
polyisoprene
Styrene-butadiene rubber –50 VG VG VG P 110 P
Polybutadiene rubber –112 G F-G E P 90 P
Butyl rubber –66 G VG G VG 60 150 P
Chlorinated butyl rubber –66 G VG G VG 60 150 P
Brominated butyl rubber –66 G VG G VG 60 150 P
Ethylene-propylene-diene monomer –55 G G G E 50 140 P
rubber
Polychloroprene –45 E E VG P 30 125 F
Nitrile rubber, medium nitrile –34 VG G E P 50 125 E
Hydrogenated nitrile rubber –30 VG G E E 30 160 E
Polyacrylate rubber –22 to –40 G G G E 10 170 E
Epichlorohydrin rubber –45 G G G E 20 135 E
Chlorinated polyethylene –25 VG G G E 150 F
Chloro-sulfonated polyethylene –25 VG VG G E 150 F
Polyester urethane rubber –35 E E E E 70 75 VG
Polyether-urethane rubber –55 E G E E 70 75 VG
Silicone rubber –120 F F F E 3 250 VG
Fluoroelastomer –18 to –50 VG G G E 20 250 E
*.E = excellent, G = good, F = fair, P = poor, V = very.
• Nitrile rubber (NBR) is resistant to most oils and some other fluids.
• Styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is used in tire treads and mechanical applications.
• Fluorinated elastomers include several types, e.g., fluorocarbons and fluorosilicones.
The elastomers can be used to 315°C, do not burn, are unaffected by most chemicals,
and have excellent electrical properties. In thermal stability and aging, only the sili-
cones are better. Physical properties are good but the cost is high.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.