Page 361 - Handbook of Plastics Technologies
P. 361
PLASTICS ADDITIVES
PLASTICS ADDITIVES 5.41
5.6.3 Chemical Foaming Agents
5.6.3.1 Sodium Bicarbonate + Citric Aid. The mixed powders are dry-coated onto
foamable polystyrene beads. When the beads are steamed to foam them, the powders dis-
solve and react to form CO . The CO is not the primary foaming agent; it is a nucleating
2
2
agent for the volatilizing pentane, serving to produce smaller and more uniform pentane
bubbles and resulting foam.
5.6.3.2 Isocyanate + Water. Flexible polyurethane foam is made primarily by the reac-
tion of excess isocyanate with a stoichiometric amount of water during the polymeriza-
tion/cure reaction. This releases CO and foams the polymer as it forms.
2
5.6.3.3 Azo Compounds. Commercial chemical foaming agents are all organic nitrogen
compounds of the general formula R-N-N-R. During the heat of melt processing, they de-
compose, liberating nitrogen and other gases. Their two most critical properties are (1) de-
composition temperature and (2) gas yield in ml from 1 g of solid foaming agent. The
leading commercial materials may be arranged by decomposition temperature (shown in
Table 5.30).
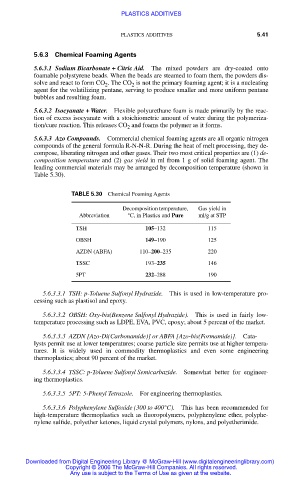
TABLE 5.30 Chemical Foaming Agents
Decomposition temperature, Gas yield in
Abbreviation °C, in Plastics and Pure ml/g at STP
TSH 105–132 115
OBSH 149–190 125
AZDN (ABFA) 110–200–235 220
TSSC 193–235 146
5PT 232–288 190
5.6.3.3.1 TSH: p-Toluene Sulfonyl Hydrazide. This is used in low-temperature pro-
cessing such as plastisol and epoxy.
5.6.3.3.2 OBSH: Oxy-bis(Benzene Sulfonyl Hydrazide). This is used in fairly low-
temperature processing such as LDPE, EVA, PVC, epoxy; about 5 percent of the market.
5.6.3.3.3 AZDN [Azo-Di(Carbonamide)] or ABFA [Azo-bis(Formamide)]. Cata-
lysts permit use at lower temperatures; coarse particle size permits use at higher tempera-
tures. It is widely used in commodity thermoplastics and even some engineering
thermoplastics; about 90 percent of the market.
5.6.3.3.4 TSSC: p-Toluene Sulfonyl Semicarbazide. Somewhat better for engineer-
ing thermoplastics.
5.6.3.3.5 5PT: 5-Phenyl Tetrazole. For engineering thermoplastics.
5.6.3.3.6 Polyphenylene Sulfoxide (300 to 400°C). This has been recommended for
high-temperature thermoplastics such as fluoropolymers, polyphenylene ether, polyphe-
nylene sulfide, polyether ketones, liquid crystal polymers, nylons, and polyetherimide.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.