Page 104 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 104
Properties of wool 85
Table 3.2 Tensile properties of fibers set at the boil for 10 min
(permanent set) or set in room temperature water for 5 min
(temporary set)
Specimen treatment
Breaking Breaking Breaking Modulus
Set Shape stress (MPa) strain (%) energy (MPa) (MPa)
Permanent Straight 175 40.5 48.8 4120
Permanent Helix 158 37.4 41.8 2280
Temporary Straight 191 43.7 56.1 4270
Temporary Helix 193 43.5 55.9 2370
Fibers tested at 65% relative humidity (Huson, 1992).
3.5.6 Effect of physical processing
The typical process of converting raw wool to fabric involves scouring, carding, gil-
ling, combing, spinning, and weaving. During all of these processes the fiber is put un-
der tension and there is the potential for strength to increase and/or damage to occur. If
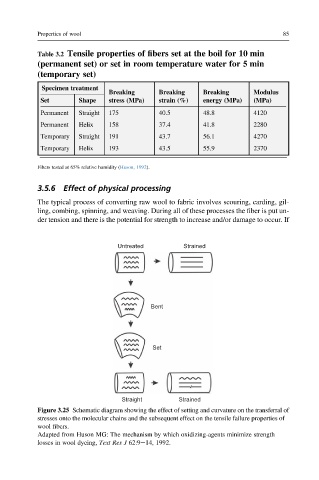
Untreated Strained
Bent
Set
Straight Strained
Figure 3.25 Schematic diagram showing the effect of setting and curvature on the transferral of
stresses onto the molecular chains and the subsequent effect on the tensile failure properties of
wool fibers.
Adapted from Huson MG: The mechanism by which oxidizing-agents minimize strength
losses in wool dyeing, Text Res J 62:9e14, 1992.