Page 260 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 260
234 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
Breaking
(Strength) point
breaking
load Yield
point
Yield F
point
Meredith (1945)
Yield
Original length L o
load
Load (F) (work of rupture) Extension Δ L Yield
Toughness
F point
Coplan and Singer
(July 1953)
θ 34
Stiffness = Yield Breaking
initial modulus elongation (%) elongation (%)
Yield point
= tan Θ
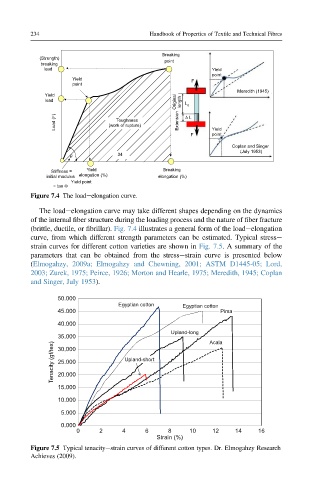
Figure 7.4 The loadeelongation curve.
The loadeelongation curve may take different shapes depending on the dynamics
of the internal fiber structure during the loading process and the nature of fiber fracture
(brittle, ductile, or fibrillar). Fig. 7.4 illustrates a general form of the loadeelongation
curve, from which different strength parameters can be estimated. Typical stresse
strain curves for different cotton varieties are shown in Fig. 7.5. A summary of the
parameters that can be obtained from the stressestrain curve is presented below
(Elmogahzy, 2009a; Elmogahzy and Chewning, 2001; ASTM D1445-05; Lord,
2003; Zurek, 1975; Peirce, 1926; Morton and Hearle, 1975; Meredith, 1945; Coplan
and Singer, July 1953).
50.000
Egyptian cotton Egyptian cotton
45.000 Pima
40.000
Upland-long
35.000 Acala
Tenacity (gf/tex) 25.000 Upland-short
30.000
20.000
15.000
10.000
5.000
0.000
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Strain (%)
Figure 7.5 Typical tenacityestrain curves of different cotton types. Dr. Elmogahzy Research
Achieves (2009).