Page 262 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 262
236 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
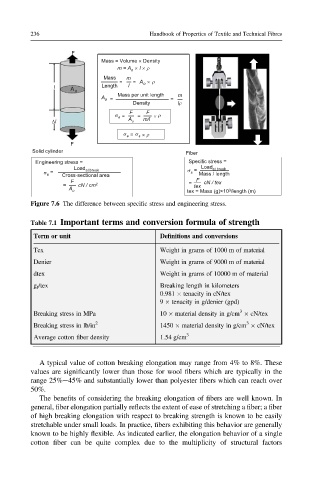
F
Mass = Volume × Density
m = A × l × ρ
o
Mass m
= = A × ρ
o
l A o Length l
A o = Mass per unit length = m
Density lρ
F F
σ e = = × ρ
Δl A o m/l
× ρ
σ e = σ s
F
Solid cylinder Fiber
Engineering stress = Specific stress =
Load Load at break
= at break σ s =
σ e Mass / length
Cross-sectional area
F = F cN / tex
= cN / cm 2 tex
A o tex = Mass (g)×10 /length (m)
3
Figure 7.6 The difference between specific stress and engineering stress.
Table 7.1 Important terms and conversion formula of strength
Term or unit Definitions and conversions
Tex Weight in grams of 1000 m of material
Denier Weight in grams of 9000 m of material
dtex Weight in grams of 10000 m of material
g f /tex Breaking length in kilometers
0.981 tenacity in cN/tex
9 tenacity in g/denier (gpd)
3
Breaking stress in MPa 10 material density in g/cm cN/tex
3
Breaking stress in lb/in 2 1450 material density in g/cm cN/tex
Average cotton fiber density 1.54 g/cm 3
A typical value of cotton breaking elongation may range from 4% to 8%. These
values are significantly lower than those for wool fibers which are typically in the
range 25%e45% and substantially lower than polyester fibers which can reach over
50%.
The benefits of considering the breaking elongation of fibers are well known. In
general, fiber elongation partially reflects the extent of ease of stretching a fiber; a fiber
of high breaking elongation with respect to breaking strength is known to be easily
stretchable under small loads. In practice, fibers exhibiting this behavior are generally
known to be highly flexible. As indicated earlier, the elongation behavior of a single
cotton fiber can be quite complex due to the multiplicity of structural factors