Page 29 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 29
10 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
so that even if the reader is not too familiar with SI units they will be able to get a feel
for how the properties of fibers is compared to other materials.
Table 1.1 gives figures that represent typical values for a range of materials,
including engineering materials; however, there is considerable scatter in the fiber sci-
ence literature, particularly for natural and regenerated fibers. One reason for this scat-
ter is the irregular cross-sections of these fibers. For many fibers their properties can be
modified by drawing or heat treatments so that they vary depending on the end use.
Table 1.1 gives values in the upper ranges of these values. For greater detail see the
relevant chapters, from which some of these values have been obtained.
Specific properties are properties divided by the specific gravity of the material.
These properties are of importance when weight is considered. It will be seen from
Table 1.1 that for most bulk materials their specific moduli fall in a narrow band
around 26 GPa. It means that if stiffness and weight are important for a structure there
is often little to be gained in terms of mechanical properties by changing one bulk ma-
terial for another. Some fibers, particularly synthetic fibers, have specific moduli that
are very much higher than those of bulk materials and this explains much of the growth
in the use of fiber-reinforced composite materials. Glass, whether in the form of fibers
or in bulk form, has a specific modulus that falls in the range of other bulk materials so
that, in terms of specific moduli some natural fibers can compete with glass fibers for
composite structures.
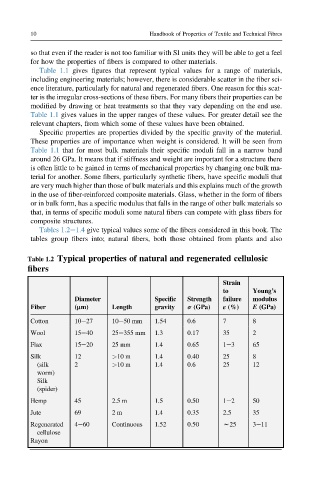
Tables 1.2e1.4 give typical values some of the fibers considered in this book. The
tables group fibers into; natural fibers, both those obtained from plants and also
Table 1.2 Typical properties of natural and regenerated cellulosic
fibers
Strain
to Young’s
Diameter Specific Strength failure modulus
Fiber (mm) Length gravity s (GPa) ε (%) E (GPa)
Cotton 10e27 10e50 mm 1.54 0.6 7 8
Wool 15e40 25e355 mm 1.3 0.17 35 2
Flax 15e20 25 mm 1.4 0.65 1e3 65
Silk 12 >10 m 1.4 0.40 25 8
(silk 2 >10 m 1.4 0.6 25 12
worm)
Silk
(spider)
Hemp 45 2.5 m 1.5 0.50 1e2 50
Jute 69 2 m 1.4 0.35 2.5 35
Regenerated 4e60 Continuous 1.52 0.50 w25 3e11
cellulose
Rayon