Page 415 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 415
388 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
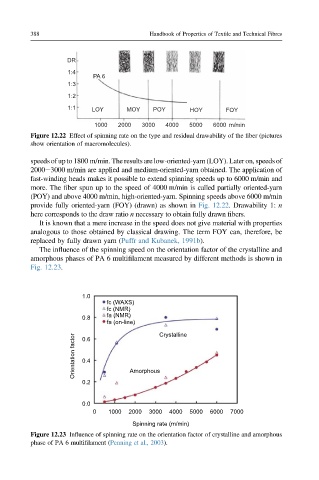
DR
1:4
PA 6
1:3
1:2
1:1 LOY MOY POY HOY FOY
1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 m/min
Figure 12.22 Effect of spinning rate on the type and residual drawability of the fiber (pictures
show orientation of macromolecules).
speeds of upto 1800 m/min.The results are low-oriented-yarn (LOY). Later on, speeds of
2000e3000 m/min are applied and medium-oriented-yarn obtained. The application of
fast-winding heads makes it possible to extend spinning speeds up to 6000 m/min and
more. The fiber spun up to the speed of 4000 m/min is called partially oriented-yarn
(POY) and above 4000 m/min, high-oriented-yarn. Spinning speeds above 6000 m/min
provide fully oriented-yarn (FOY) (drawn) as shown in Fig. 12.22. Drawability 1: n
here corresponds to the draw ratio n necessary to obtain fully drawn fibers.
It is known that a mere increase in the speed does not give material with properties
analogous to those obtained by classical drawing. The term FOY can, therefore, be
replaced by fully drawn yarn (Puffr and Kubanek, 1991b).
The influence of the spinning speed on the orientation factor of the crystalline and
amorphous phases of PA 6 multifilament measured by different methods is shown in
Fig. 12.23.
1.0
fc (WAXS)
fc (NMR)
fa (NMR)
0.8
fa (on-line) Crystalline
Orientation factor 0.6
0.4
0.2 Amorphous
0.0
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000
Spinning rate (m/min)
Figure 12.23 Influence of spinning rate on the orientation factor of crystalline and amorphous
phase of PA 6 multifilament (Penning et al., 2003).