Page 463 - Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
P. 463
436 Handbook of Properties of Textile and Technical Fibres
connected to the number-averaged molecular weight M n of PET by the Mark Houwink
equation:
½h¼ KM a (13.3)
n
5
where a ¼ 0.898 and K ¼ 5.41$10 dL/g, were found by regression for high
molecular weight of PET and solvent dichloromethane/trifluoroacetic acid (Huang
et al., 1994). The molecular weight corresponding to intrinsic viscosity (h) ¼ 0.8 dL/g
is M ¼ 44,000 and for viscosity (h) ¼ 0.9 dL/g is M ¼ 50,200.
The delivery pump must provide a pressure of about 100e200 bars to force the flow
through the pack, which contains filtration media (e.g., sand) to remove any particles
larger than a few mm.
Standard spinning nozzles have holes of 0.1e1 mm in diameter. The polymer
throughput per hole is usually in the range of le5 g/hole min. The extrusion velocity,
i.e., exit velocity from the spinneret v B (m/min) depends on the amount of melt mass
passing through the hole, hole diameter, and density of the melt. Typical values of v B
are about 10e30 m/min (Fourné, 1999).
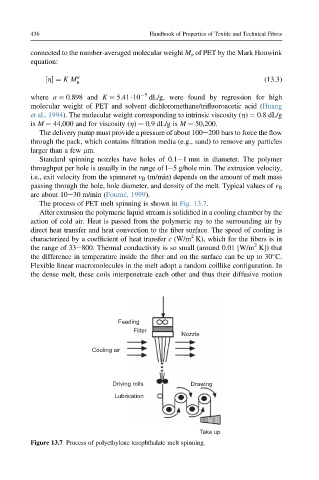
The process of PET melt spinning is shown in Fig. 13.7.
After extrusion the polymeric liquid stream is solidified in a cooling chamber by the
action of cold air. Heat is passed from the polymeric ray to the surrounding air by
direct heat transfer and heat convection to the fiber surface. The speed of cooling is
2
characterized by a coefficient of heat transfer c (W/m K), which for the fibers is in
2
the range of 33e800. Thermal conductivity is so small (around 0.01 [W/m K]) that
the difference in temperature inside the fiber and on the surface can be up to 30 C.
Flexible linear macromolecules in the melt adopt a random coillike configuration. In
the dense melt, these coils interpenetrate each other and thus their diffusive motion
Feeding
Filter
Nozzle
Cooling air
Driving rolls Drawing
Lubrication
Take up
Figure 13.7 Process of polyethylene terephthalate melt spinning.