Page 103 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 103
98 Surface Tension and Wetting
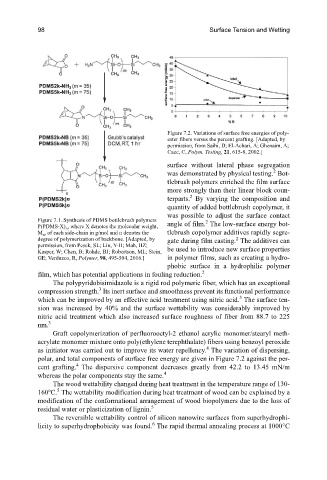
Figure 7.2. Variations of surface free energies of poly-
ester fibers versus the percent grafting. [Adapted, by
permission, from Saihi, D; El-Achari, A; Ghenaim, A;
Caze, C, Polym. Testing, 21, 615-8, 2002.]
surface without lateral phase segregation
2
was demonstrated by physical testing. Bot-
tlebrush polymers enriched the film surface
more strongly than their linear block coun-
2
terparts. By varying the composition and
quantity of added bottlebrush copolymer, it
was possible to adjust the surface contact
Figure 7.1. Synthesis of PDMS bottlebrush polymers angle of film. The low-surface energy bot-
2
P(PDMS-X) , where X denotes the molecular weight,
n
M , of each side-chain in g/mol and n denotes the tlebrush copolymer additives rapidly segre-
n
degree of polymerization of backbone. [Adapted, by gate during film casting. The additives can
2
permission, from Pesek, SL; Lin, Y-H; Mah, HZ; be used to introduce new surface properties
Kasper, W; Chen, B; Rohde, BJ; Robertson, ML; Stein,
GE; Verduzco, R, Polymer, 98, 495-504, 2016.] in polymer films, such as creating a hydro-
phobic surface in a hydrophilic polymer
2
film, which has potential applications in fouling reduction.
The polypyridobisimidazole is a rigid rod polymeric fiber, which has an exceptional
3
compression strength. Its inert surface and smoothness prevent its functional performance
3
which can be improved by an effective acid treatment using nitric acid. The surface ten-
sion was increased by 40% and the surface wettability was considerably improved by
nitric acid treatment which also increased surface roughness of fiber from 88.7 to 225
3
nm.
Graft copolymerization of perfluorooctyl-2 ethanol acrylic monomer/stearyl meth-
acrylate monomer mixture onto poly(ethylene terephthalate) fibers using benzoyl peroxide
4
as initiator was carried out to improve its water repellency. The variation of dispersing,
polar, and total components of surface free energy are given in Figure 7.2 against the per-
4
cent grafting. The dispersive component decreases greatly from 42.2 to 13.45 mN/m
4
whereas the polar components stay the same.
The wood wettability changed during heat treatment in the temperature range of 130-
o
5
160 C. The wettability modification during heat treatment of wood can be explained by a
modification of the conformational arrangement of wood biopolymers due to the loss of
5
residual water or plasticization of lignin.
The reversible wettability control of silicon nanowire surfaces from superhydrophi-
6
licity to superhydrophobicity was found. The rapid thermal annealing process at 1000°C