Page 185 - Handbook of Surface Improvement and Modification
P. 185
180 The Coefficient of Friction
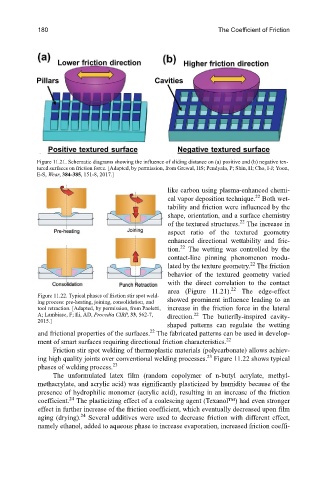
Figure 11.21. Schematic diagrams showing the influence of sliding distance on (a) positive and (b) negative tex-
tured surfaces on friction force. [Adapted, by permission, from Grewal, HS; Pendyala, P; Shin, H; Cho, I-J; Yoon,
E-S, Wear, 384-385, 151-8, 2017.]
like carbon using plasma-enhanced chemi-
22
cal vapor deposition technique. Both wet-
tability and friction were influenced by the
shape, orientation, and a surface chemistry
22
of the textured structures. The increase in
aspect ratio of the textured geometry
enhanced directional wettability and fric-
22
tion. The wetting was controlled by the
contact-line pinning phenomenon modu-
22
lated by the texture geometry. The friction
behavior of the textured geometry varied
with the direct correlation to the contact
22
area (Figure 11.21). The edge-effect
Figure 11.22. Typical phases of friction stir spot weld- showed prominent influence leading to an
ing process: pre-heating, joining, consolidation, and
tool retraction. [Adapted, by permission, from Paoletti, increase in the friction force in the lateral
A; Lambiase, F; Ili, AD, Procedia CIRP, 33, 562-7, direction. The butterfly-inspired cavity-
22
2015.]
shaped patterns can regulate the wetting
22
and frictional properties of the surfaces. The fabricated patterns can be used in develop-
22
ment of smart surfaces requiring directional friction characteristics.
Friction stir spot welding of thermoplastic materials (polycarbonate) allows achiev-
23
ing high quality joints over conventional welding processes. Figure 11.22 shows typical
23
phases of welding process.
The unformulated latex film (random copolymer of n-butyl acrylate, methyl-
methacrylate, and acrylic acid) was significantly plasticized by humidity because of the
presence of hydrophilic monomer (acrylic acid), resulting in an increase of the friction
24
coefficient. The plasticizing effect of a coalescing agent (Texanol™) had even stronger
effect in further increase of the friction coefficient, which eventually decreased upon film
24
aging (drying). Several additives were used to decrease friction with different effect,
namely ethanol, added to aqueous phase to increase evaporation, increased friction coeffi-