Page 199 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 199
168 So l i d - S t at e La s e r s Intr oduction to h igh-Power Solid-State Lasers 169
HAP SSLs. First, as described above, is YAG’s favorable material prop-
erties, along with its ability to readily accept dopant concentrations
exceeding 1 percent Nd and up to 100 percent (stoichiometric) Yb.
10
Second, both Ndand Yb exhibit favorable spectroscopic characteristics
that are amenable to diode pumping and that result in highly efficient
conversion of pump light to laser light.
Nd:YAG
Nd:YAG is historically the most common SSL gain material, having
found widespread application in lamp-pumped rod lasers. This four-
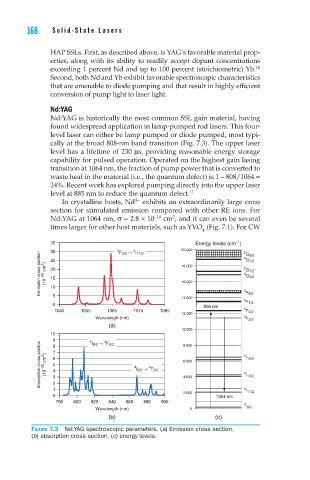
level laser can either be lamp pumped or diode pumped, most typi-
cally at the broad 808-nm band transition (Fig. 7.3). The upper laser
level has a lifetime of 230 µs, providing reasonable energy storage
capability for pulsed operation. Operated on the highest gain lasing
transition at 1064 nm, the fraction of pump power that is converted to
waste heat in the material (i.e., the quantum defect) is 1 – 808/1064 =
24%. Recent work has explored pumping directly into the upper laser
level at 885 nm to reduce the quantum defect. 11
3+
In crystalline hosts, Nd exhibits an extraordinarily large cross
section for stimulated emission compared with other RE ions. For
2
–19
Nd:YAG at 1064 nm, σ = 2.8 × 10 cm , and it can even be several
times larger for other host materials, such as YVO (Fig. 7.1). For CW
4
−1
35 4 F 3/2 → I 11/2 20,000 Energy levels (cm ) 2 G 9/2
4
30
Emission cross section (10 −20 cm 2 ) 25 18,000 4 2 4 G 7/2
20
G 7/2
G 5/2
15
16,000
10
5
14,000 4 F 9/2
4
0 F 7/2
808 nm
1045 1055 1065 1075 1085 4 F 5/2
12,000
Wavelength (nm) 4 F 3/2
(a)
10,000
10
9 8 4 I 9/2 → F 5/2 8,000
4
Absorption cross section (10 −20 cm 2 ) 7 6 5 4 3 4 I 9/2 → F 3/2 6,000 4 4 I 15/2
4
I 13/2
1 2 4,000 4
2,000 I 11/2
0 1064 nm
780 800 820 840 860 880 900
4
Wavelength (nm) 0 I 9/2
(b) (c)
Figure 7.3 Nd:YAG spectroscopic parameters. (a) Emission cross section,
(b) absorption cross section, (c) energy levels.