Page 258 - High Power Laser Handbook
P. 258
226 So l i d - S t at e La s e r s Thin-Disc Lasers 227
Laser beam
Pump power
Pumped area
AR coating
Laser active material
HR coating
Heat flow
Heat sink
Surface cooling
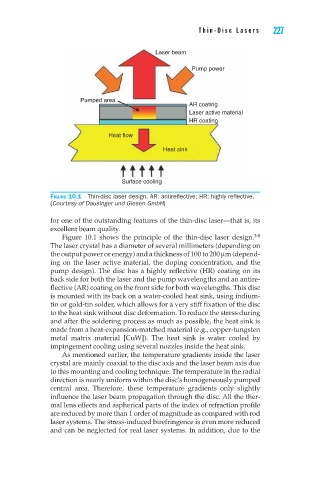
Figure 10.1 Thin-disc laser design. AR: antireflective; HR: highly reflective.
(Courtesy of Dausinger und Giesen GmbH)
for one of the outstanding features of the thin-disc laser—that is, its
excellent beam quality.
Figure 10.1 shows the principle of the thin-disc laser design.
3-8
The laser crystal has a diameter of several millimeters (depending on
the output power or energy) and a thickness of 100 to 200 mm (depend-
ing on the laser active material, the doping concentration, and the
pump design). The disc has a highly reflective (HR) coating on its
back side for both the laser and the pump wavelengths and an antire-
flective (AR) coating on the front side for both wavelengths. This disc
is mounted with its back on a water-cooled heat sink, using indium-
tin or gold-tin solder, which allows for a very stiff fixation of the disc
to the heat sink without disc deformation. To reduce the stress during
and after the soldering process as much as possible, the heat sink is
made from a heat-expansion-matched material (e.g., copper-tungsten
metal matrix material [CuW]). The heat sink is water cooled by
impingement cooling using several nozzles inside the heat sink.
As mentioned earlier, the temperature gradients inside the laser
crystal are mainly coaxial to the disc axis and the laser beam axis due
to this mounting and cooling technique. The temperature in the radial
direction is nearly uniform within the disc’s homogeneously pumped
central area. Therefore, these temperature gradients only slightly
influence the laser beam propagation through the disc. All the ther-
mal lens effects and aspherical parts of the index of refraction profile
are reduced by more than 1 order of magnitude as compared with rod
laser systems. The stress-induced birefringence is even more reduced
and can be neglected for real laser systems. In addition, due to the