Page 61 - Highway Engineering Handbook Building and Rehabilitating the Infrastructure
P. 61
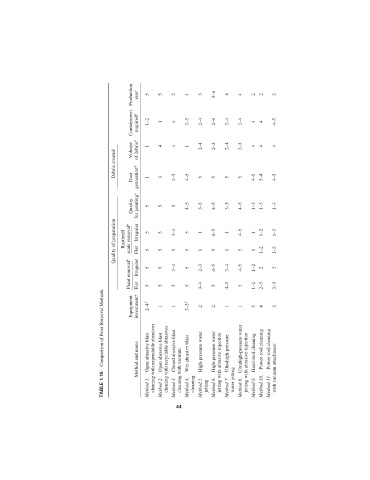
Production rate e 5 5 2 4 3 3–4 4 4 2 2 2
Containment required d 1–2 1 4 2–3 2–4 2–4 2–4 2–4 4 4 4–5
Debris created Volume Dust of debris d generation d 1 1 4 3 4 4–5 1 4–5 2–4 5 2–3 5 2–4 5 2–3 5 4 4–5 4 3–4 4 4–5
Quality for painting c 5 5 5 4–5 3–5 4–5 3–5 4–5 1–3 1–3 1–3
Quality of preparation Rust/mill scale removal b Irregular Flat 5 5 5 5 3–4 5 5 5 1 1 4–5 5 1 1 4–5 5 1 1 1–2 1–2 1–2 1–2
Paint removal b Irregular Flat 5 5 5 5 3–4 5 5 5 2–3 3–4 4–5 5 3–4 4–5 4–5 5 1–2 1–2 2 2–3 2 2–3
Comparison of Paint Removal Methods Equipment investment a 2–4 f Open abrasive blast 1 Open abrasive blast 1 Closed abrasive blast 2–3 f Wet abrasive blast 2 High-pressure water 2 High-pressure water 1 Ultrahigh-pressure 1 Ultrahigh-pressure water 5 Hand-tool cleaning 4 Power-tool cleaning Power-tool cleaning 3
TABLE 1.15 Method and name Method 1. cleaning with expendable abrasives Method 2. cleaning with recyclable abrasives Method 3. cleaning with vacuum Method 4. cleaning Method 5. jetting Method 6. jetting with abrasive injection Method 7. water jetting Method 8. jetting with abrasive injection Method 9. Method 10. Method 11. with vacuum attachment
44