Page 193 - Human Inspired Dexterity in Robotic Manipulation
P. 193
192 Human Inspired Dexterity in Robotic Manipulation
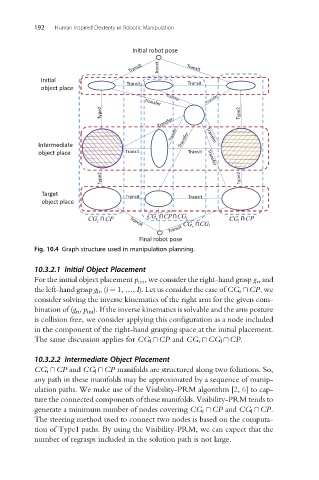
Fig. 10.4 Graph structure used in manipulation planning.
10.3.2.1 Initial Object Placement
For the initial object placement p ini , we consider the right-hand grasp g ri and
the left-hand grasp g li ,(i ¼ 1, …, I). Let us consider the case of CG r \CP,we
consider solving the inverse kinematics of the right arm for the given com-
bination of (g ri , p ini ). If the inverse kinematics is solvable and the arm posture
is collision free, we consider applying this configuration as a node included
in the component of the right-hand grasping space at the initial placement.
The same discussion applies for CG l \CP and CG r \CG l \CP.
10.3.2.2 Intermediate Object Placement
CG r \CP and CG l \CP manifolds are structured along two foliations. So,
any path in these manifolds may be approximated by a sequence of manip-
ulation paths. We make use of the Visibility-PRM algorithm [2, 6] to cap-
ture the connected components of these manifolds. Visibility-PRM tends to
generate a minimum number of nodes covering CG r \CP and CG l \CP.
The steering method used to connect two nodes is based on the computa-
tion of Type1 paths. By using the Visibility-PRM, we can expect that the
number of regrasps included in the solution path is not large.