Page 91 - Human Inspired Dexterity in Robotic Manipulation
P. 91
Approaching Human Hand Dexterity Through Highly Biomimetic Design 89
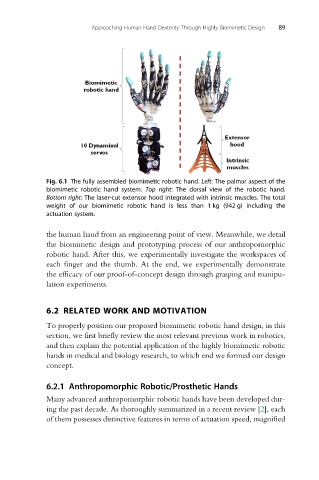
Fig. 6.1 The fully assembled biomimetic robotic hand. Left: The palmar aspect of the
biomimetic robotic hand system. Top right: The dorsal view of the robotic hand.
Bottom right: The laser-cut extensor hood integrated with intrinsic muscles. The total
weight of our biomimetic robotic hand is less than 1 kg (942 g) including the
actuation system.
the human hand from an engineering point of view. Meanwhile, we detail
the biomimetic design and prototyping process of our anthropomorphic
robotic hand. After this, we experimentally investigate the workspaces of
each finger and the thumb. At the end, we experimentally demonstrate
the efficacy of our proof-of-concept design through grasping and manipu-
lation experiments.
6.2 RELATED WORK AND MOTIVATION
To properly position our proposed biomimetic robotic hand design, in this
section, we first briefly review the most relevant previous work in robotics,
and then explain the potential application of the highly biomimetic robotic
hands in medical and biology research, to which end we formed our design
concept.
6.2.1 Anthropomorphic Robotic/Prosthetic Hands
Many advanced anthropomorphic robotic hands have been developed dur-
ing the past decade. As thoroughly summarized in a recent review [2], each
of them possesses distinctive features in terms of actuation speed, magnified