Page 17 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 17
CHAPTER 1 History of Low-Salinity and Smart Waterflood 9
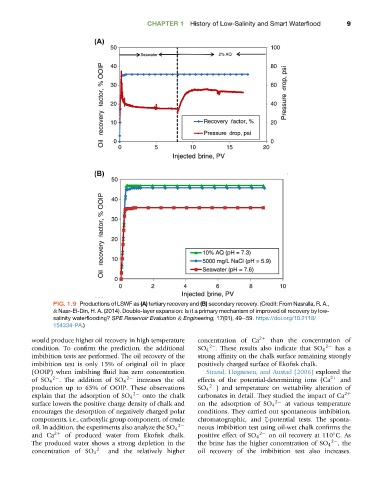
FIG. 1.9 Productions of LSWF as (A) tertiary recovery and (B) secondary recovery. (Credit: From Nasralla, R. A.,
& Nasr-El-Din, H. A. (2014). Double-layer expansion: Is it a primary mechanism of improved oil recovery by low-
salinity waterflooding? SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 17(01), 49e59. https://doi.org/10.2118/
154334-PA.)
would produce higher oil recovery in high temperature concentration of Ca 2þ than the concentration of
condition. To confirm the prediction, the additional SO 4 2 . These results also indicate that SO 4 2 has a
imbibition tests are performed. The oil recovery of the strong affinity on the chalk surface remaining strongly
imbibition test is only 15% of original oil in place positively charged surface of Ekofisk chalk.
(OOIP) when imbibing fluid has zero concentration Strand, Høgnesen, and Austad (2006) explored the
2 2 increases the oil effects of the potential-determining ions (Ca 2þ and
of SO 4 . The addition of SO 4
production up to 65% of OOIP. These observations SO 4 2 ) and temperature on wettability alteration of
2 2þ
explain that the adsorption of SO 4 onto the chalk carbonates in detail. They studied the impact of Ca
surface lowers the positive charge density of chalk and on the adsorption of SO 4 2 at various temperature
encourages the desorption of negatively charged polar conditions. They carried out spontaneous imbibition,
components, i.e., carboxylic group component, of crude chromatographic, and z-potential tests. The sponta-
2
oil. In addition, the experiments also analyze the SO 4 neous imbibition test using oil-wet chalk confirms the
and Ca 2þ of produced water from Ekofisk chalk. positive effect of SO 4 2 on oil recovery at 110 C. As
The produced water shows a strong depletion in the the brine has the higher concentration of SO 4 2 , the
2
concentration of SO 4 and the relatively higher oil recovery of the imbibition test also increases.