Page 90 - Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart Waterflooding
P. 90
82 Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery using Smart Waterflooding
low-permeable carbonates. The study also was interested
P. Inlet P. BS 1 P. BS 2 Brine change Frac. production rate Matrix production rate
160 Low Sal. 1 7 in the diversion of flow path and gel-blocking capacity,
Low Sal. 2 Low Sal. 3 FW not wettability modification, when LSWF was deployed
140 6
120 5 as the chasing water. The polymer gel fills the fracture
Pressure (kPa) 100 4 3 Production Rate (mL/hr) lows the fluid flow through the fracture channel. After the
volume reducing the fracture conductivity, but it still al-
gel treatment, LSWF as chasing water injection expects to
80
60
ture channeling restoring matrix flow. This study tried
2 improve the gel-blocking capacity and reduces the frac-
40
to demonstrate these expectations by measuring the in-
P
R 1
20 jection pressure and matrix production rate from core-
0 0 flooding and visualizing flow paths from positron
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 emission tomography (PET)-CT scanner. In the core-
Time (FV)
flooding, chasing water injection using high-salinity
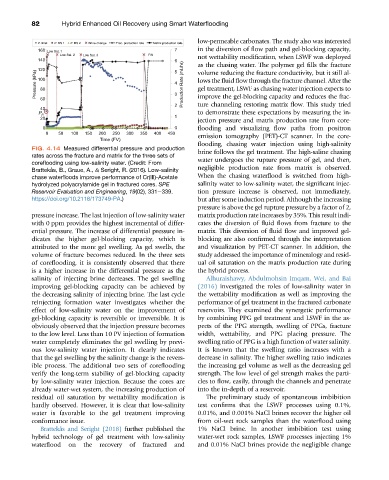
FIG. 4.14 Measured differential pressure and production
brine follows the gel treatment. The high-saline chasing
rates across the fracture and matrix for the three sets of
water undergoes the rupture pressure of gel, and then,
coreflooding using low-salinity water. (Credit: From
Brattekås, B., Graue, A., & Seright, R. (2016). Low-salinity negligible production rate from matrix is observed.
chase waterfloods improve performance of Cr(III)-Acetate When the chasing waterflood is switched from high-
hydrolyzed polyacrylamide gel in fractured cores. SPE salinity water to low-salinity water, the significant injec-
Reservoir Evaluation and Engineering, 19(02), 331e339. tion pressure increase is observed, not immediately,
https://doi.org/10.2118/173749-PA.) but after some induction period. Although the increasing
pressure is above the gel rupture pressure by a factor of 2,
pressure increase. The last injection of low-salinity water matrix production rate increases by 35%. This result indi-
with 0 ppm provides the highest incremental of differ- cates the diversion of fluid flows from fracture to the
ential pressure. The increase of differential pressure in- matrix. This diversion of fluid flow and improved gel-
dicates the higher gel-blocking capacity, which is blocking are also confirmed through the interpretation
attributed to the more gel swelling. As gel swells, the and visualization by PET-CT scanner. In addition, the
volume of fracture becomes reduced. In the three sets study addressed the importance of mineralogy and resid-
of coreflooding, it is consistently observed that there ual oil saturation on the matrix production rate during
is a higher increase in the differential pressure as the the hybrid process.
salinity of injecting brine decreases. The gel swelling Alhuraishawy, Abdulmohsin Imqam, Wei, and Bai
improving gel-blocking capacity can be achieved by (2016) investigated the roles of low-salinity water in
the decreasing salinity of injecting brine. The last cycle the wettability modification as well as improving the
reinjecting formation water investigates whether the performance of gel treatment in the fractured carbonate
effect of low-salinity water on the improvement of reservoirs. They examined the synergetic performance
gel-blocking capacity is reversible or irreversible. It is by combining PPG gel treatment and LSWF in the as-
obviously observed that the injection pressure becomes pects of the PPG strength, swelling of PPGs, fracture
to the low level. Less than 10 PV injection of formation width, wettability, and PPG placing pressure. The
water completely eliminates the gel swelling by previ- swelling ratio of PPG is a high function of water salinity.
ous low-salinity water injection. It clearly indicates It is known that the swelling ratio increases with a
that the gel swelling by the salinity change is the revers- decrease in salinity. The higher swelling ratio indicates
ible process. The additional two sets of coreflooding the increasing gel volume as well as the decreasing gel
verify the long-term stability of gel-blocking capacity strength. The low level of gel strength makes the parti-
by low-salinity water injection. Because the cores are cles to flow, easily, through the channels and penetrate
already water-wet system, the increasing production of into the in-depth of a reservoir.
residual oil saturation by wettability modification is The preliminary study of spontaneous imbibition
hardly observed. However, it is clear that low-salinity test confirms that the LSWF processes using 0.1%,
water is favorable to the gel treatment improving 0.01%, and 0.001% NaCl brines recover the higher oil
conformance issue. from oil-wet rock samples than the waterflood using
Brattekås and Seright (2018) further published the 1% NaCl brine. In another imbibition test using
hybrid technology of gel treatment with low-salinity water-wet rock samples, LSWF processes injecting 1%
waterflood on the recovery of fractured and and 0.01% NaCl brines provide the negligible change