Page 48 - Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
P. 48
32 Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
dynamics of a big, grid-connected microgrid structure is found to be very complex.
Analysis of such complex dynamics is difficult to be carried out by linear methods.
Therefore nonlinear techniques have been proposed and applied for the analysis of
hierarchical control based microgrid structures. These nonlinear approaches are also
called Coherency-based methods. In this method, first, coherent group of generators
are identified. Thereafter, coherent generators are aggregated into one single unit and
connected to one equivalent bus. Finally, remaining buses are eliminated to reduce the
overall size of network.
5.1 Droop-based control of microgrid
Hierarchical control discussed in the previous section requires a number of informa-
tion to be communicated between different microgrids and among individual micro-
sources. This necessitates a dedicated communication system for microgrid operation.
Consortium for Electrical Reliability Technology Solutions (CERTS) has established
that a without communication microgrid structure is a desired microgrid structure.
In a without communication microgrid operation, control scheme should be capable
of taking a decision for specific microsource without the data from other sources.
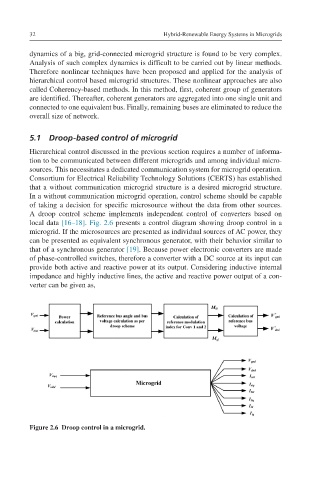
A droop control scheme implements independent control of converters based on
local data [16–18]. Fig. 2.6 presents a control diagram showing droop control in a
microgrid. If the microsources are presented as individual sources of AC power, they
can be presented as equivalent synchronous generator, with their behavior similar to
that of a synchronous generator [19]. Because power electronic converters are made
of phase-controlled switches, therefore a converter with a DC source at its input can
provide both active and reactive power at its output. Considering inductive internal
impedance and highly inductive lines, the active and reactive power output of a con-
verter can be given as,
Figure 2.6 Droop control in a microgrid.