Page 52 - Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
P. 52
36 Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
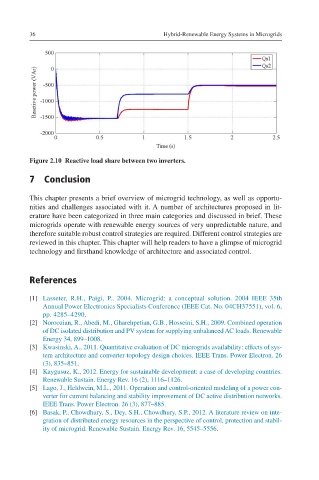
Figure 2.10 Reactive load share between two inverters.
7 Conclusion
This chapter presents a brief overview of microgrid technology, as well as opportu-
nities and challenges associated with it. A number of architectures proposed in lit-
erature have been categorized in three main categories and discussed in brief. These
microgrids operate with renewable energy sources of very unpredictable nature, and
therefore suitable robust control strategies are required. Different control strategies are
reviewed in this chapter. This chapter will help readers to have a glimpse of microgrid
technology and firsthand knowledge of architecture and associated control.
References
[1] Lasseter, R.H., Paigi, P., 2004. Microgrid: a conceptual solution. 2004 IEEE 35th
Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37551), vol. 6,
pp. 4285–4290.
[2] Noroozian, R., Abedi, M., Gharehpetian, G.B., Hosseini, S.H., 2009. Combined operation
of DC isolated distribution and PV system for supplying unbalanced AC loads. Renewable
Energy 34, 899–1008.
[3] Kwasinski, A., 2011. Quantitative evaluation of DC microgrids availability: effects of sys-
tem architecture and converter topology design choices. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26
(3), 835–851.
[4] Kaygusuz, K., 2012. Energy for sustainable development: a case of developing countries.
Renewable Sustain. Energy Rev. 16 (2), 1116–1126.
[5] Lago, J., Heldwein, M.L., 2011. Operation and control-oriented modeling of a power con-
verter for current balancing and stability improvement of DC active distribution networks.
IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26 (3), 877–885.
[6] Basak, P., Chowdhury, S., Dey, S.H., Chowdhury, S.P., 2012. A literature review on inte-
gration of distributed energy resources in the perspective of control, protection and stabil-
ity of microgrid. Renewable Sustain. Energy Rev. 16, 5545–5556.