Page 56 - Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
P. 56
40 Hybrid-Renewable Energy Systems in Microgrids
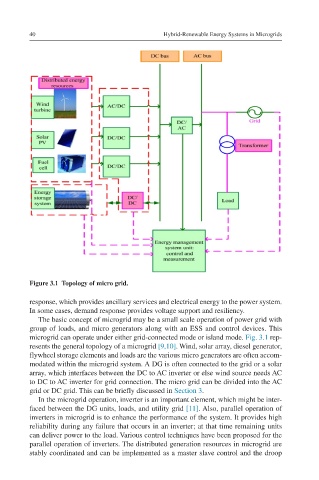
Figure 3.1 Topology of micro grid.
response, which provides ancillary services and electrical energy to the power system.
In some cases, demand response provides voltage support and resiliency.
The basic concept of microgrid may be a small scale operation of power grid with
group of loads, and micro generators along with an ESS and control devices. This
microgrid can operate under either grid-connected mode or island mode. Fig. 3.1 rep-
resents the general topology of a microgrid [9,10]. Wind, solar array, diesel generator,
flywheel storage elements and loads are the various micro generators are often accom-
modated within the microgrid system. A DG is often connected to the grid or a solar
array, which interfaces between the DC to AC inverter or else wind source needs AC
to DC to AC inverter for grid connection. The micro grid can be divided into the AC
grid or DC grid. This can be briefly discussed in Section 3.
In the microgrid operation, inverter is an important element, which might be inter-
faced between the DG units, loads, and utility grid [11]. Also, parallel operation of
inverters in microgrid is to enhance the performance of the system. It provides high
reliability during any failure that occurs in an inverter; at that time remaining units
can deliver power to the load. Various control techniques have been proposed for the
parallel operation of inverters. The distributed generation resources in microgrid are
stably coordinated and can be implemented as a master slave control and the droop