Page 281 - Hydrocarbon
P. 281
268 Oil and Gas Processing
Table 11.1 Typical product specifications
Oil True vapour pressure (TVP) o83 kPa @ 151
Base sediment and water (BS&W) o0.5 vol%
Temperature WPour point
Salinity (NaCl) o70 g/m 3
3
Hydrogen sulphide (H 2 S) o70 g/m
Gas Liquid content o100 mg/m 3
Water dew point at 51C o7Pa
Heating value W25 MJ/m 3
Composition, CO 2 ,N 2 ,H 2 S
Delivery pressure and temperature
Water Dispersed oil content o40 ppm
Suspended solids content o50 g/m 3
gas
separation
production
and
from dew point
wells treatment conditioning
oil
contaminant
degassing removal
water
de-oiling dehydration compression
disposal evacuation evacuation
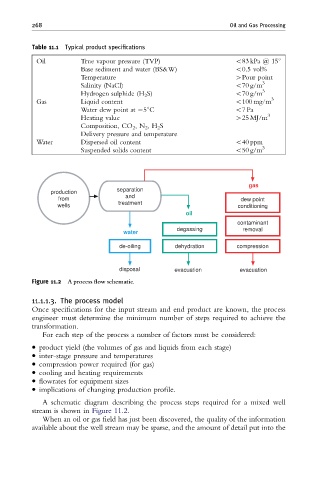
Figure 11.2 A process £ow schematic.
11.1.1.3. The process model
Once specifications for the input stream and end product are known, the process
engineer must determine the minimum number of steps required to achieve the
transformation.
For each step of the process a number of factors must be considered:
product yield (the volumes of gas and liquids from each stage)
inter-stage pressure and temperatures
compression power required (for gas)
cooling and heating requirements
flowrates for equipment sizes
implications of changing production profile.
A schematic diagram describing the process steps required for a mixed well
stream is shown in Figure 11.2.
When an oil or gas field has just been discovered, the quality of the information
available about the well stream may be sparse, and the amount of detail put into the