Page 116 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 116
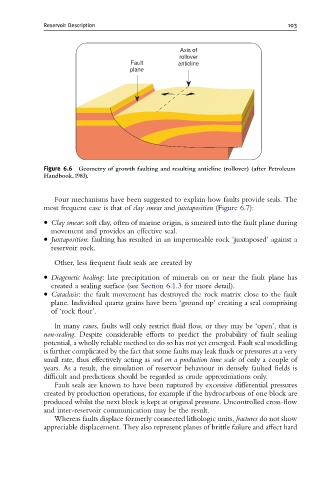
Reservoir Description 103
Axis of
rollover
Fault anticline
plane
Figure 6.6 Geometry of growth faulting and resulting anticline (rollover) (after Petroleum
Handbook,1983).
Four mechanisms have been suggested to explain how faults provide seals. The
most frequent case is that of clay smear and juxtaposition (Figure 6.7):
Clay smear: soft clay, often of marine origin, is smeared into the fault plane during
movement and provides an effective seal.
Juxtaposition: faulting has resulted in an impermeable rock ‘juxtaposed’ against a
reservoir rock.
Other, less frequent fault seals are created by
Diagenetic healing: late precipitation of minerals on or near the fault plane has
created a sealing surface (see Section 6.1.3 for more detail).
Cataclasis: the fault movement has destroyed the rock matrix close to the fault
plane. Individual quartz grains have been ‘ground up’ creating a seal comprising
of ‘rock flour’.
In many cases, faults will only restrict fluid flow, or they may be ‘open’, that is
non-sealing. Despite considerable efforts to predict the probability of fault sealing
potential, a wholly reliable method to do so has not yet emerged. Fault seal modelling
is further complicated by the fact that some faults may leak fluids or pressures at a very
small rate, thus effectively acting as seal on a production time scale of only a couple of
years. As a result, the simulation of reservoir behaviour in densely faulted fields is
difficult and predictions should be regarded as crude approximations only.
Fault seals are known to have been ruptured by excessive differential pressures
created by production operations, for example if the hydrocarbons of one block are
produced whilst the next block is kept at original pressure. Uncontrolled cross-flow
and inter-reservoir communication may be the result.
Whereas faults displace formerly connected lithologic units, fractures do not show
appreciable displacement. They also represent planes of brittle failure and affect hard