Page 117 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 117
104 Reservoir Geology
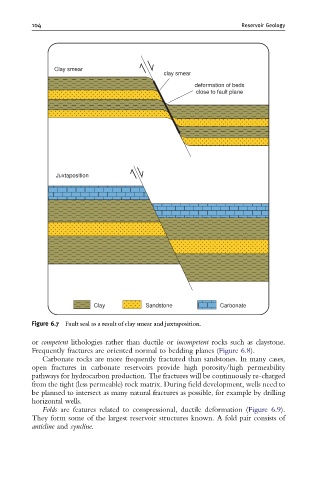
Clay smear
clay smear
deformation of beds
close to fault plane
Juxtaposition
Clay Sandstone Carbonate
Figure 6.7 Fault seal as a result of clay smear and juxtaposition.
or competent lithologies rather than ductile or incompetent rocks such as claystone.
Frequently fractures are oriented normal to bedding planes (Figure 6.8).
Carbonate rocks are more frequently fractured than sandstones. In many cases,
open fractures in carbonate reservoirs provide high porosity/high permeability
pathways for hydrocarbon production. The fractures will be continuously re-charged
from the tight (less permeable) rock matrix. During field development, wells need to
be planned to intersect as many natural fractures as possible, for example by drilling
horizontal wells.
Folds are features related to compressional, ductile deformation (Figure 6.9).
They form some of the largest reservoir structures known. A fold pair consists of
anticline and syncline.