Page 143 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 143
130 Reservoir Fluids
sample which requires recombining to recreate the reservoir fluid. Both sampling
techniques face the same problem of trying to capture a representative sample (i.e. the
correct proportion of gas to oil) when the pressure falls below the bubble point.
6.2.6.1. Subsurface samples
Subsurface samples can be taken with a subsurface sampling chamber, called a
sampling bomb, or with a formation pressure testing tool (RFT, MDT, RCI), all of
which are devices run on wireline to the reservoir depth. These tools are further
described in Section 6.3.6.
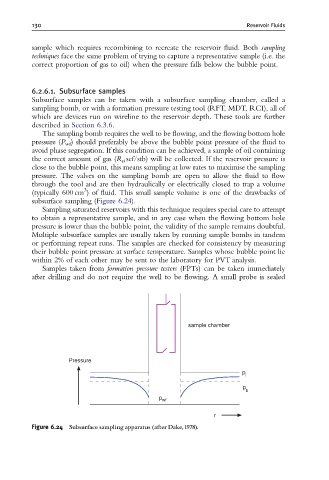
The sampling bomb requires the well to be flowing, and the flowing bottom hole
pressure (P wf ) should preferably be above the bubble point pressure of the fluid to
avoid phase segregation. If this condition can be achieved, a sample of oil containing
the correct amount of gas (R si scf/stb) will be collected. If the reservoir pressure is
close to the bubble point, this means sampling at low rates to maximise the sampling
pressure. The valves on the sampling bomb are open to allow the fluid to flow
through the tool and are then hydraulically or electrically closed to trap a volume
3
(typically 600 cm ) of fluid. This small sample volume is one of the drawbacks of
subsurface sampling (Figure 6.24).
Sampling saturated reservoirs with this technique requires special care to attempt
to obtain a representative sample, and in any case when the flowing bottom hole
pressure is lower than the bubble point, the validity of the sample remains doubtful.
Multiple subsurface samples are usually taken by running sample bombs in tandem
or performing repeat runs. The samples are checked for consistency by measuring
their bubble point pressure at surface temperature. Samples whose bubble point lie
within 2% of each other may be sent to the laboratory for PVT analysis.
Samples taken from formation pressure testers (FPTs) can be taken immediately
after drilling and do not require the well to be flowing. A small probe is sealed
sample chamber
Pressure
p
i
p
b
p
wf
r
Figure 6.24 Subsurface sampling apparatus (after Dake,1978).