Page 151 - Hydrocarbon Exploration and Production Second Edition
P. 151
138 Reservoir Fluids
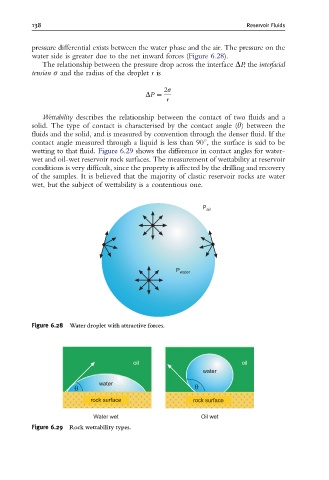
pressure differential exists between the water phase and the air. The pressure on the
water side is greater due to the net inward forces (Figure 6.28).
The relationship between the pressure drop across the interface DP, the interfacial
tension s and the radius of the droplet r is
2s
DP ¼
r
Wettability describes the relationship between the contact of two fluids and a
solid. The type of contact is characterised by the contact angle (y) between the
fluids and the solid, and is measured by convention through the denser fluid. If the
contact angle measured through a liquid is less than 901, the surface is said to be
wetting to that fluid. Figure 6.29 shows the difference in contact angles for water-
wet and oil-wet reservoir rock surfaces. The measurement of wettability at reservoir
conditions is very difficult, since the property is affected by the drilling and recovery
of the samples. It is believed that the majority of clastic reservoir rocks are water
wet, but the subject of wettability is a contentious one.
P air
P water
Figure 6.28 Water droplet with attractive forces.
Figure 6.29 Rock wettability types.