Page 242 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 242
HYDC06 12/5/05 5:34 PM Page 225
Groundwater quality and contaminant hydrogeology 225
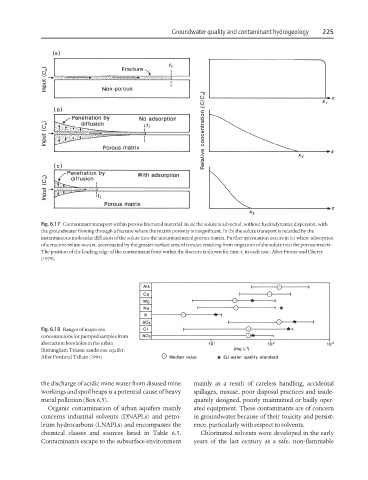
Fig. 6.17 Contaminant transport within porous fractured material. In (a) the solute is advected, without hydrodynamic dispersion, with
the groundwater flowing through a fracture where the matrix porosity is insignificant. In (b) the solute transport is retarded by the
instantaneous molecular diffusion of the solute into the uncontaminated porous matrix. Further attenuation occurs in (c) where adsorption
of a reactive solute occurs, accentuated by the greater surface area of contact resulting from migration of the solute into the porous matrix.
The position of the leading edge of the contaminant front within the fracture is shown for time t in each case. After Freeze and Cherry
1
(1979).
Fig. 6.18 Ranges of major ion
concentrations for pumped samples from
abstraction boreholes in the urban
Birmingham Triassic sandstone aquifer.
After Ford and Tellam (1994).
the discharge of acidic mine water from disused mine mainly as a result of careless handling, accidental
workings and spoil heaps is a potential cause of heavy spillages, misuse, poor disposal practices and inade-
metal pollution (Box 6.5). quately designed, poorly maintained or badly oper-
Organic contamination of urban aquifers mainly ated equipment. These contaminants are of concern
concerns industrial solvents (DNAPLs) and petro- in groundwater because of their toxicity and persist-
leum hydrocarbons (LNAPLs) and encompasses the ence, particularly with respect to solvents.
chemical classes and sources listed in Table 6.5. Chlorinated solvents were developed in the early
Contaminants escape to the subsurface environment years of the last century as a safe, non-flammable