Page 248 - Hydrogeology Principles and Practice
P. 248
HYDC06 12/5/05 5:34 PM Page 231
Groundwater quality and contaminant hydrogeology 231
Table 6.6 Summary of chlorinated solvents detected in groundwater in the Birmingham Triassic sandstone aquifer. Solvent abbreviations
are given in Table 6.3. After Rivett et al. (1990).
Industrial solvents TCE TCA PCE TCM CTET
% boreholes with solvent detected 78 46 44 53 37
Proportion of boreholes exceeding (%)
1 mgL −1 62 22 9 17 2
10 mgL −1 43 13 4 0 0
100 mgL −1 30 5 2 0 0
−1
Maximum concentration detected (mgL ) 5500 780 460 5 1
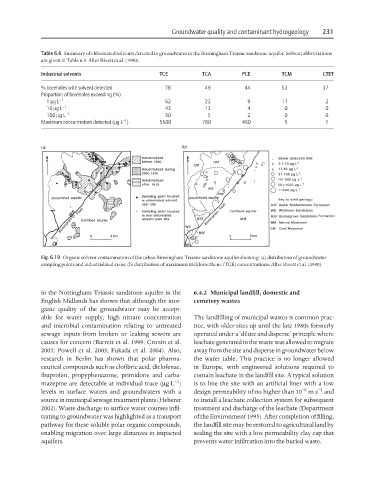
Fig. 6.19 Organic solvent contamination of the urban Birmingham Triassic sandstone aquifer showing: (a) distribution of groundwater
sampling points and industrialized areas; (b) distribution of maximum trichloroethene (TCE) concentrations. After Rivett et al. (1990).
in the Nottingham Triassic sandstone aquifer in the 6.4.2 Municipal landfill, domestic and
English Midlands has shown that although the inor- cemetery wastes
ganic quality of the groundwater may be accept-
able for water supply, high nitrate concentration The landfilling of municipal wastes is common prac-
and microbial contamination relating to untreated tice, with older sites up until the late 1980s formerly
sewage inputs from broken or leaking sewers are operated under a ‘dilute and disperse’ principle where
causes for concern (Barrett et al. 1999; Cronin et al. leachate generated in the waste was allowed to migrate
2003; Powell et al. 2003; Fukada et al. 2004). Also, away from the site and disperse in groundwater below
research in Berlin has shown that polar pharma- the water table. This practice is no longer allowed
ceutical compounds such as clofibric acid, diclofenac, in Europe, with engineered solutions required to
ibuprofen, propyphenazone, primidone and carba- contain leachate in the landfill site. A typical solution
−1
mazepine are detectable at individual trace (µgL ) is to line the site with an artificial liner with a low
−1
−9
levels in surface waters and groundwaters with a design permeability of no higher than 10 ms and
source in municipal sewage treatment plants (Heberer to install a leachate collection system for subsequent
2002). Waste discharge to surface water courses infil- treatment and discharge of the leachate (Department
trating to groundwater was highlighted as a transport of the Environment 1995). After completion of filling,
pathway for these soluble polar organic compounds, the landfill site may be restored to agricultural land by
enabling migration over large distances in impacted sealing the site with a low permeability clay cap that
aquifers. prevents water infiltration into the buried waste.