Page 105 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 105
102 INDETERMINATE ERROR
indeterminate error Random error that can be identified by
statistical means and then minimized or eliminated.
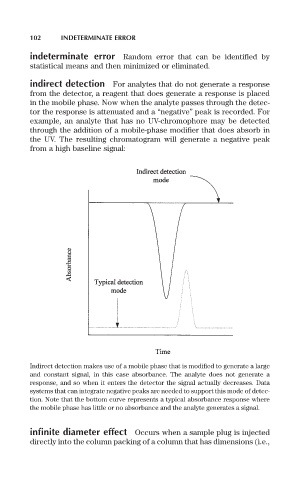
indirect detection For analytes that do not generate a response
from the detector, a reagent that does generate a response is placed
in the mobile phase. Now when the analyte passes through the detec-
tor the response is attenuated and a “negative” peak is recorded. For
example, an analyte that has no UV-chromophore may be detected
through the addition of a mobile-phase modifier that does absorb in
the UV. The resulting chromatogram will generate a negative peak
from a high baseline signal:
Indirect detection makes use of a mobile phase that is modified to generate a large
and constant signal, in this case absorbance. The analyte does not generate a
response, and so when it enters the detector the signal actually decreases. Data
systems that can integrate negative peaks are needed to support this mode of detec-
tion. Note that the bottom curve represents a typical absorbance response where
the mobile phase has little or no absorbance and the analyte generates a signal.
infinite diameter effect Occurs when a sample plug is injected
directly into the column packing of a column that has dimensions (i.e.,