Page 136 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 136
NORMALITY, N 135
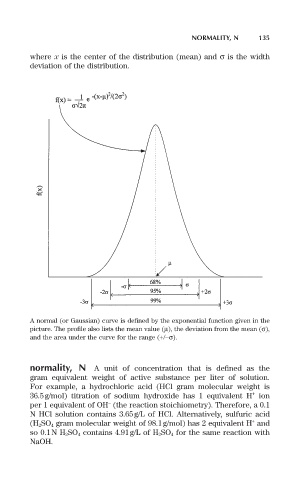
where x is the center of the distribution (mean) and s is the width
deviation of the distribution.
A normal (or Gaussian) curve is defined by the exponential function given in the
picture. The profile also lists the mean value (m), the deviation from the mean (s),
and the area under the curve for the range (+/-s).
normality, N A unit of concentration that is defined as the
gram equivalent weight of active substance per liter of solution.
For example, a hydrochloric acid (HCl gram molecular weight is
+
36.5g/mol) titration of sodium hydroxide has 1 equivalent H ion
-
per 1 equivalent of OH (the reaction stoichiometry). Therefore, a 0.1
N HCl solution contains 3.65g/L of HCl. Alternatively, sulfuric acid
+
(H 2SO 4 gram molecular weight of 98.1g/mol) has 2 equivalent H and
so 0.1N H 2 SO 4 contains 4.91g/L of H 2 SO 4 for the same reaction with
NaOH.