Page 38 - Illustrated Pocket Dictionary of Chromatography
P. 38
CHROMATOGRAPH 33
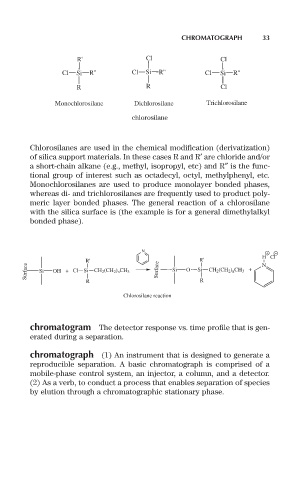
R' Cl Cl
Cl Si R'' Cl Si R'' Cl Si R''
R R Cl
Monochlorosilane Dichlorosilane Trichlorosilane
chlorosilane
Chlorosilanes are used in the chemical modification (derivatization)
of silica support materials. In these cases R and R¢ are chloride and/or
a short-chain alkane (e.g., methyl, isopropyl, etc) and R≤ is the func-
tional group of interest such as octadecyl, octyl, methylphenyl, etc.
Monochlorosilanes are used to produce monolayer bonded phases,
whereas di- and trichlorosilanes are frequently used to product poly-
meric layer bonded phases. The general reaction of a chlorosilane
with the silica surface is (the example is for a general dimethylalkyl
bonded phase).
N
H Cl
R' R' N
Surface Si OH + Cl Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3 Surface Si O Si CH 2 (CH 2 ) n CH 3 +
R R
Chlorosilane reaction
chromatogram The detector response vs. time profile that is gen-
erated during a separation.
chromatograph (1) An instrument that is designed to generate a
reproducible separation. A basic chromatograph is comprised of a
mobile-phase control system, an injector, a column, and a detector.
(2) As a verb, to conduct a process that enables separation of species
by elution through a chromatographic stationary phase.