Page 147 - Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
P. 147
4.3 HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER 109
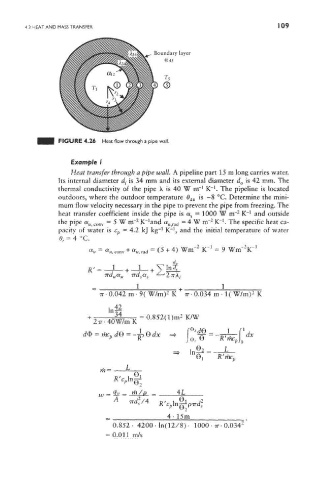
FIGURE 4.26 Heat flow through a pipe wall.
Example I
Heat transfer through a pipe wall. A pipeline part 15m long carries water.
Its internal diameter d i is 34 mm and its external diameter d 0 is 42 mm. The
1
]
thermal conductivity of the pipe X is 40 W m~ K" . The pipeline is located
outdoors, where the outdoor temperature B ao is -8 °C. Determine the mini-
mum flow velocity necessary in the pipe to prevent the pipe from freezing. The
2
1
heat transfer coefficient inside the pipe is a s = 1000 W m~ Kr and outside
2
1
-1
2
the pipe a u conv = 5 W m~ K and a u racj = 4 W m~ K" . The specific heat ca-
1
1
pacity of water is c^ — 4.2 kj kg" K* , and the initial temperature of water
0,- = 4 °C.