Page 180 - Industrial Ventilation Design Guidebook
P. 180
1 42 CHAPTER 4 PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS
radiation drier, this approach is reasonable if the radiation energy is ab-
sorbed evenly inside the web. Assuming the boundary layers on both sides
of the web are similar, the vapor flow is distributed symmetrically to the
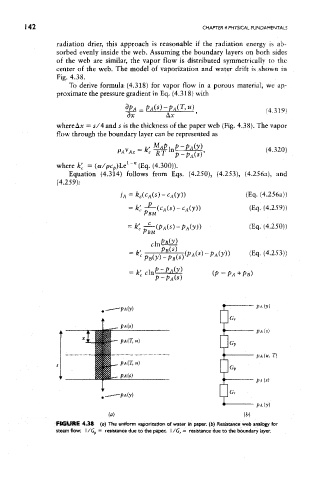
center of the web. The model of vaporization and water drift is shown in
Fig. 4.38.
To derive formula (4.318) for vapor flow in a porous material, we ap-
proximate the pressure gradient in Eq. (4.318) with
where Ax = s/4 and s is the thickness of the paper web (Fig. 4.38). The vapor
flow through the boundary layer can be represented as
l n
where k' c = (a/pc p)Lt ~ (Eq. (4.300)).
Equation (4.314) follows from Eqs. (4.250), (4.253), (4.256a), and
(4.259):
FIGURE 4.38 (a) The uniform vaporization of water in paper, (b) Resistance web analogy for
steam flow; I /G p = resistance due to the paper, I /G r = resistance due to the boundary layer.