Page 157 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 157
Advanced Physico-chemical Methods of Treatment for Industrial Wastewaters 131
100
Nearly 100% ammoniacal nitrogen can
be removed
80
% Reduction 60
40
20
0
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7
Industrial effluent treatment using cavitation
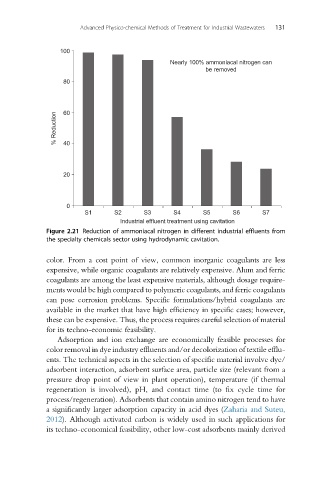
Figure 2.21 Reduction of ammoniacal nitrogen in different industrial effluents from
the specialty chemicals sector using hydrodynamic cavitation.
color. From a cost point of view, common inorganic coagulants are less
expensive, while organic coagulants are relatively expensive. Alum and ferric
coagulants are among the least expensive materials, although dosage require-
ments would be high compared to polymeric coagulants, and ferric coagulants
can pose corrosion problems. Specific formulations/hybrid coagulants are
available in the market that have high efficiency in specific cases; however,
these can be expensive. Thus, the process requires careful selection of material
for its techno-economic feasibility.
Adsorption and ion exchange are economically feasible processes for
color removal in dye industry effluents and/or decolorization of textile efflu-
ents. The technical aspects in the selection of specific material involve dye/
adsorbent interaction, adsorbent surface area, particle size (relevant from a
pressure drop point of view in plant operation), temperature (if thermal
regeneration is involved), pH, and contact time (to fix cycle time for
process/regeneration). Adsorbents that contain amino nitrogen tend to have
a significantly larger adsorption capacity in acid dyes (Zaharia and Suteu,
2012). Although activated carbon is widely used in such applications for
its techno-economical feasibility, other low-cost adsorbents mainly derived