Page 24 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 24
Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse: An Overview 7
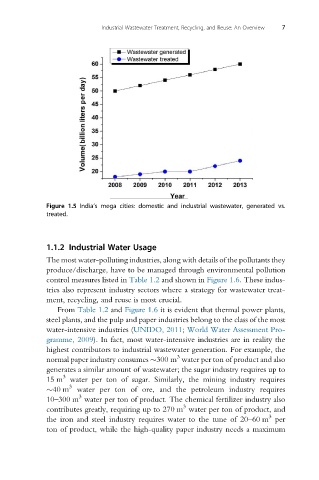
Figure 1.5 India’s mega cities: domestic and industrial wastewater, generated vs.
treated.
1.1.2 Industrial Water Usage
The most water-polluting industries, along with details of the pollutants they
produce/discharge, have to be managed through environmental pollution
control measures listed in Table 1.2 and shown in Figure 1.6. These indus-
tries also represent industry sectors where a strategy for wastewater treat-
ment, recycling, and reuse is most crucial.
From Table 1.2 and Figure 1.6 it is evident that thermal power plants,
steel plants, and the pulp and paper industries belong to the class of the most
water-intensive industries (UNIDO, 2011; World Water Assessment Pro-
gramme, 2009). In fact, most water-intensive industries are in reality the
highest contributors to industrial wastewater generation. For example, the
3
normal paper industry consumes 300 m water per ton of product and also
generates a similar amount of wastewater; the sugar industry requires up to
3
15 m water per ton of sugar. Similarly, the mining industry requires
3
40 m water per ton of ore, and the petroleum industry requires
3
10–300 m water per ton of product. The chemical fertilizer industry also
3
contributes greatly, requiring up to 270 m water per ton of product, and
3
the iron and steel industry requires water to the tune of 20–60 m per
ton of product, while the high-quality paper industry needs a maximum