Page 43 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 43
26 Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse
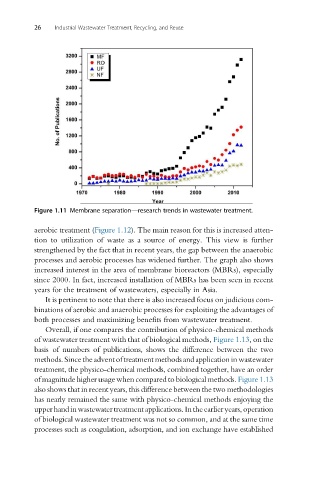
Figure 1.11 Membrane separation—research trends in wastewater treatment.
aerobic treatment (Figure 1.12). The main reason for this is increased atten-
tion to utilization of waste as a source of energy. This view is further
strengthened by the fact that in recent years, the gap between the anaerobic
processes and aerobic processes has widened further. The graph also shows
increased interest in the area of membrane bioreactors (MBRs), especially
since 2000. In fact, increased installation of MBRs has been seen in recent
years for the treatment of wastewaters, especially in Asia.
It is pertinent to note that there is also increased focus on judicious com-
binations of aerobic and anaerobic processes for exploiting the advantages of
both processes and maximizing benefits from wastewater treatment.
Overall, if one compares the contribution of physico-chemical methods
of wastewater treatment with that of biological methods, Figure 1.13, on the
basis of numbers of publications, shows the difference between the two
methods. Since the adventoftreatment methods and application in wastewater
treatment, the physico-chemical methods, combined together, have an order
of magnitude higher usage when compared to biological methods. Figure 1.13
also shows that in recent years, this difference between the two methodologies
has nearly remained the same with physico-chemical methods enjoying the
upperhandinwastewatertreatmentapplications.Intheearlieryears,operation
of biological wastewater treatment was not so common, and at the same time
processes such as coagulation, adsorption, and ion exchange have established