Page 98 - Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling and Reuse
P. 98
Industrial Wastewater Treatment, Recycling, and Reuse: An Overview 73
High treatment cost
Incineration
More specificity
Wet air oxidation
Treatment cost Cavitation Adsorption/ion exchange More difficulty
Membranes
Biological treatment
Coagulation
Effluent volume treated
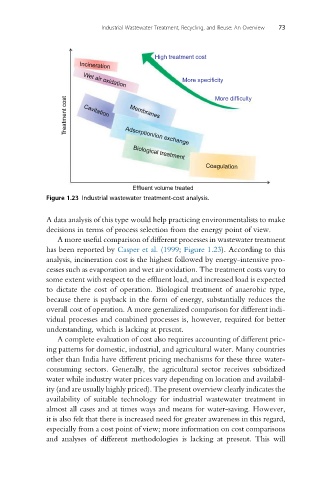
Figure 1.23 Industrial wastewater treatment-cost analysis.
A data analysis of this type would help practicing environmentalists to make
decisions in terms of process selection from the energy point of view.
A more useful comparison of different processes in wastewater treatment
has been reported by Casper et al. (1999; Figure 1.23). According to this
analysis, incineration cost is the highest followed by energy-intensive pro-
cesses such as evaporation and wet air oxidation. The treatment costs vary to
some extent with respect to the effluent load, and increased load is expected
to dictate the cost of operation. Biological treatment of anaerobic type,
because there is payback in the form of energy, substantially reduces the
overall cost of operation. A more generalized comparison for different indi-
vidual processes and combined processes is, however, required for better
understanding, which is lacking at present.
A complete evaluation of cost also requires accounting of different pric-
ing patterns for domestic, industrial, and agricultural water. Many countries
other than India have different pricing mechanisms for these three water-
consuming sectors. Generally, the agricultural sector receives subsidized
water while industry water prices vary depending on location and availabil-
ity (and are usually highly priced). The present overview clearly indicates the
availability of suitable technology for industrial wastewater treatment in
almost all cases and at times ways and means for water-saving. However,
it is also felt that there is increased need for greater awareness in this regard,
especially from a cost point of view; more information on cost comparisons
and analyses of different methodologies is lacking at present. This will