Page 174 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 174
166 S. Rathinam and R. Sengupta
Once, this path is followed, the UAV reaches the position (¯x(d j ), ¯(d j )) at
y
some final angle θ and this angle is chosen as the heading at the final position.
The algorithm MV A for the RAP(m) is as follows:
1. Construct a complete graph with vertices being all the UAVs and desti-
nations. Assign the Euclidean distance as the cost to each edge that joins
a UAV to a destination and a destination to a destination. Assign zero
cost to an edge that joins any two UAVs.
2. Find the minimum spanning tree of the graph using Prim’s algorithm [2].
This minimum spanning tree will contain exactly m − 1 zero cost edges
where m is the number of UAVs (Fig. 17).
3. Remove the zero cost edges to get a tree for each UAV (Fig. 18).
4. For each tree corresponding to a UAV, double its edges to construct a
Eulerian graph (Fig. 19). Then construct a tour for each UAV based on
the Eulerian graph. A tour for each UAV is a sequence of destinations for
it to visit (Fig. 20). (This step is similar to tour construction for the single
TSP discussed in section 2.3).
5. Use the above sequence and construct paths using algorithm S between
any two consecutive locations. For example, use algorithm S to construct
a path from (x(v 1 ),y(v 1 ),α 1 )to(¯x(d 1 ), ¯y(d 1 )). Say, the UAV reaches the
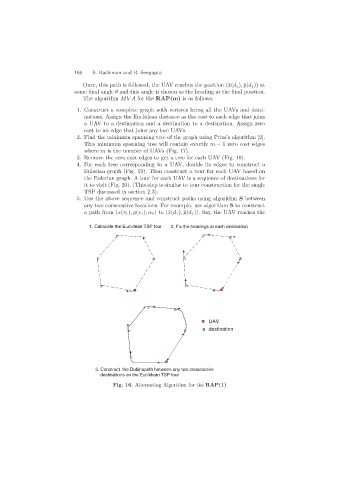
1. Calculate the Euclidean TSP tour 2. Fix the headings at each destination
UAV
destination
3. Construct the Dubinspath between any two consecutive
destinations on the Euclidean TSP tour
Fig. 16. Alternating Algorithm for the RAP(1)