Page 123 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry : Fundamentals and Applications
P. 123
Inductively Coupled Pla,~~a Mass Spectrometry 113
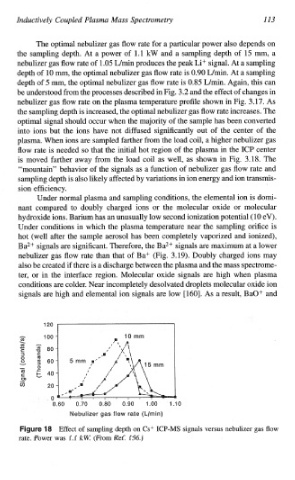
The optimal nebulizer gas flow rate for a particular power also depends on
the sampling depth. At a power of 1.1 kW and a sampling depth of 15 mm, a
nebulizer gas flow rate of 1.05 L/min produces the peak Li+ signal. At a sampling
depth of 10 mm, the optimal nebulizer gas flow rate is 0.90 L/min. At a sampling
depth of 5 mm, the optimal nebulizer gas flow rate is 0.85 L/min. Again, this can
of
be understood from the processes described in Fig. 3.2 and the effect changes in
nebulizer gas flow rate on the plasma temperature profile shown in Fig. 3.17. As
the sampling depth is increased, the optimal nebulizer gas flow rate increases.
The
of
optimal signal should occur when the majority the sample has been converted
into ions but the ions have not diffused significantly out of the center of the
plasma. When ions are sampled farther from the load coil, a higher nebulizer gas
flow rate is needed so that the initial hot region of the plasma in the ICP center
is moved farther away from the load coil as well, as shown in Fig. 3.18. The
“mountain,’ behavior of the signals as a function of nebulizer gas flow rate and
sampling depth is also likely affected by variations in ion energy and ion
transmis-
sion efficiency.
Under normal plasma and sampling conditions, the elemental ion is domi-
nant compared to doubly charged ions or the molecular oxide or molecular
hydroxide ions. Barium has an unusually low second ionization potential eV).
(10
Under conditions in which the plasma temperature near the sampling orifice is
hot (well after the sample aerosol has been completely vaporized and ionized),
Ba2+ signals are significant, Therefore, the Ba2+ signals are maximum at a lower
nebulizer gas flow rate than that of Ba+ (Fig. 3.19). Doubly charged ions may
also be created if there is a discharge between the plasma and the mass spectrome-
ter, or in the interface region. Molecular oxide signals are high when plasma
conditions are colder. Near incompletely desolvated droplets molecular oxide ion
signals are high and elemental ion signals are low [ 1601. As a result, BaO+ and
100 -f 10 mm
80
60
40
20
0
0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 1.00 1 IO
Nebulizer gas flow rate (Llmin)
Effect of sampling depth on CS+ ICP-MS signals versus nebulizer gas flow
rate. Power was 1 .l kW. (From Ref. 156.)