Page 165 - Instant notes
P. 165
The motion of larger ions 151
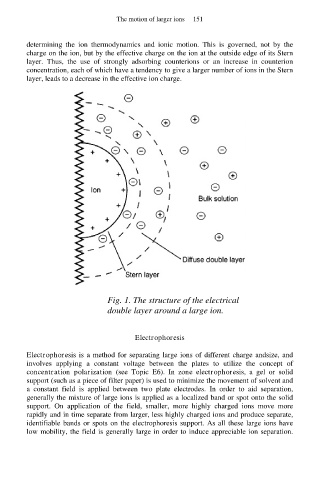
determining the ion thermodynamics and ionic motion. This is governed, not by the
charge on the ion, but by the effective charge on the ion at the outside edge of its Stern
layer. Thus, the use of strongly adsorbing counterions or an increase in counterion
concentration, each of which have a tendency to give a larger number of ions in the Stern
layer, leads to a decrease in the effective ion charge.
Fig. 1. The structure of the electrical
double layer around a large ion.
Electrophoresis
Electrophoresis is a method for separating large ions of different charge andsize, and
involves applying a constant voltage between the plates to utilize the concept of
concentration polarization (see Topic E6). In zone electrophoresis, a gel or solid
support (such as a piece of filter paper) is used to minimize the movement of solvent and
a constant field is applied between two plate electrodes. In order to aid separation,
generally the mixture of large ions is applied as a localized band or spot onto the solid
support. On application of the field, smaller, more highly charged ions move more
rapidly and in time separate from larger, less highly charged ions and produce separate,
identifiable bands or spots on the electrophoresis support. As all these large ions have
low mobility, the field is generally large in order to induce appreciable ion separation.