Page 270 - Instant notes
P. 270
Physical chemistry 256
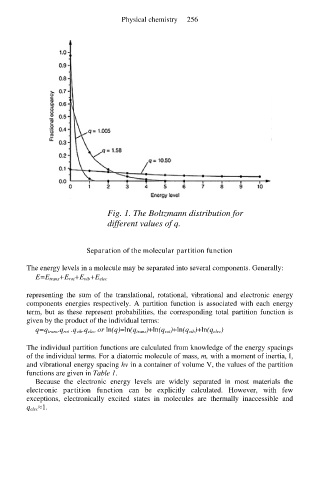
Fig. 1. The Boltzmann distribution for
different values of q.
Separation of the molecular partition function
The energy levels in a molecule may be separated into several components. Generally:
E=E trans+E rot+E υib+E elec
representing the sum of the translational, rotational, vibrational and electronic energy
components energies respectively. A partition function is associated with each energy
term, but as these represent probabilities, the corresponding total partition function is
given by the product of the individual terms:
q=q trans.q rot .q vib.q elec or ln(q)=ln(q trans)+ln(q rot)+ln(q vib)+ln(q elec)
The individual partition functions are calculated from knowledge of the energy spacings
of the individual terms. For a diatomic molecule of mass, m, with a moment of inertia, I,
and vibrational energy spacing hv in a container of volume V, the values of the partition
functions are given in Table 1.
Because the electronic energy levels are widely separated in most materials the
electronic partition function can be explicitly calculated. However, with few
exceptions, electronically excited states in molecules are thermally inaccessible and
q elec≈1.