Page 266 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 266
L1644_C06.fm Page 239 Monday, October 20, 2003 12:06 PM
data of local air emissions
(predominant pollutants)
Site-specific (air): calculation of factors
Fate and exposure analysis
generic generic or
detailed?
detailed
optional
Integrated Impact Integrated Impact Local/ Gaussian
Assessment model Assessment model Local/ Gaussian Dispersion model
(e.g., EcoSense 2.0) (e.g., EcoSense 2.0) Dispersion model (e.g., BEEST/ISCST-3)
Dispersion and long- (e.g., BEEST/ISCST-3) Multimedia fate model
range transport model Long-range transport (e.g., UNIRISK)
(e.g., ISCST-2 and WTM) model (e.g., WTM) EUSES, CalTOX
consequence consequence consequence consequence
analysis analysis analysis analysis
optional
uncertainty
analysis
(e.g., by
Monte Carlo
Simulation)
individual
(cancer) risk
Sum of physical impact multiplication
parameter like cancer cases with exposed
population
(cancer) cases
compare
(cancer) cases
impact factors for fate and exposure and
consequence analysis
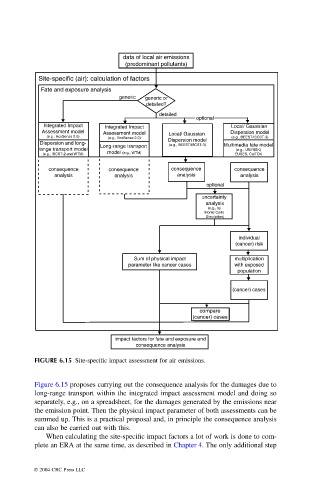
FIGURE 6.15 Site-specific impact assessment for air emissions.
Figure 6.15 proposes carrying out the consequence analysis for the damages due to
long-range transport within the integrated impact assessment model and doing so
separately, e.g., on a spreadsheet, for the damages generated by the emissions near
the emission point. Then the physical impact parameter of both assessments can be
summed up. This is a practical proposal and, in principle the consequence analysis
can also be carried out with this.
When calculating the site-specific impact factors a lot of work is done to com-
plete an ERA at the same time, as described in Chapter 4. The only additional step
© 2004 CRC Press LLC