Page 295 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 295
L1644_C07.fm Page 267 Monday, October 20, 2003 12:10 PM
emitted I nm =D RE nm / M n . The index i refers to an emission situation rather than
pr i,, pr i,, pi,
to an emission site only. The emission situation is determined by the emission site
and by the source type such as the stack height for emissions to air or the release
depth into the lake or river for emissions to water.
DD nm = E m ◊ M n I ◊ nm (7.4)
pr i,, pr, pi, pr i,,
where
DD nm is the incremental damage caused (damage) due to the emission of pol-
pr i,,
lutant p into the initial medium n (air, water or soil), at the emission
situation i, on the receptor r in the target compartment m (air, water,
soil or food chain).
M n is the mass of pollutant p (kg) emitted into the initial medium n (air, water
pi,
or soil) at the emission situation i.
I nm is the incremental receptor exposure per mass of pollutant emitted (recep-
pr i
,,
3
tors.(mg/m ).yr/kg) due to the amount of pollutant p emitted into the
initial medium n (air, water or soil) at the emission situation i on the
receptor r in the target compartment m (air, water, soil or food chain).
The mass of pollutant emitted, M, the fate and exposure factor, F, the effect
factor, E, and the effective receptor density, r , used in the presented framework
eff
are directly related to the causality chain illustrated in Figure 7.2. Such a compre-
hensive framework is the basis for using high levels of sophistication in the different
dimensions of impact information corresponding to the scheme described in Figure
7.1.
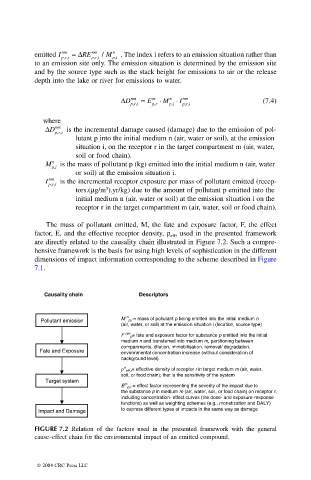
Causality chain Descriptors
n
M p,i = mass of pollutant p being emitted into the initial medium n
Pollutant emission
(air, water, or soil) at the emission situation i (location, source type)
F nm p = fate and exposure factor for substance p emitted into the initial
medium n and transferred into medium m, partitioning between
compartments, dilution, immobilisation, removal/ degradation,
Fate and Exposure environmental concentration increase (without consideration of
background level)
n
ρ eff,r = effective density of receptor r in target medium m (air, water,
soil, or food chain); that is the sensitivity of the system
Target system
m
E p,r = effect factor representing the severity of the impact due to
the substance p in medium m (air, water, soil, or food chain) on receptor r,
including concentration- effect curves (the dose- and exposure-response
functions) as well as weighting schemes (e.g., monetization and DALY)
to express different types of impacts in the same way as damage
Impact and Damage
FIGURE 7.2 Relation of the factors used in the presented framework with the general
cause–effect chain for the environmental impact of an emitted compound.
© 2004 CRC Press LLC