Page 348 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 348
L1644_C08.fm Page 313 Tuesday, October 21, 2003 3:03 PM
99.6
4.3
-- continued
13.1
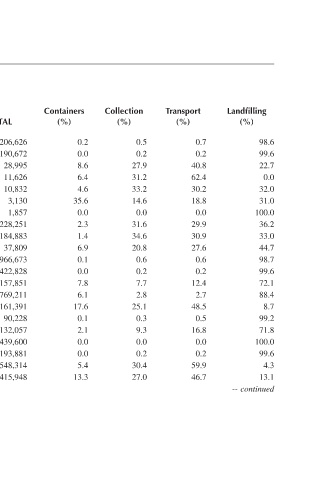
Landfilling (%) 98.6 99.6 22.7 0.0 32.0 31.0 100.0 36.2 33.0 44.7 98.7 99.6 72.1 88.4 8.7 99.2 71.8 100.0
Transport (%) 0.7 0.2 40.8 62.4 30.2 18.8 0.0 29.9 30.9 27.6 0.6 0.2 12.4 2.7 48.5 0.5 16.8 0.0 0.2 59.9 46.7
Collection (%) 0.5 0.2 27.9 31.2 33.2 14.6 0.0 31.6 34.6 20.8 0.6 0.2 7.7 2.8 25.1 0.3 9.3 0.0 0.2 30.4 27.0
Containers (%) 0.2 0.0 8.6 6.4 4.6 35.6 0.0 2.3 1.4 6.9 0.1 0.0 7.8 6.1 17.6 0.1 2.1 0.0 0.0 5.4 13.3
TOTAL 1,206,626 1,190,672 28,995 11,626 10,832 3,130 1,857 228,251 184,883 37,809 64,802,966,673 63,338,422,828 1,157,851 769,211 161,391 90,228 173,132,057 65,439,600 48,193,881 42,548,314 6,271,415,948
Characterization factors * 0.42 * 40.29 0.0557 0.117 0.115 * 0.0217 0.0313 * 64 * 4,500 16,000 84 * 1,200 17 67000 —
Impact Assessment of Landfilling Activity a
Impacts Water eutrophication (g eq. PO 4 ) Depletion of nonrenewable resources (yr -1 ) (a) Nitrogen oxides (NOx as NO 2 ) Greenhouse effect (direct, 20 years) (g equiv. CO 2 ) Aquatic eco-toxicity (g equiv. 1-4-dichlorobenzene) Human toxicity (g equiv. 1-4-dichlorobenzene) (a) Trichloroethane (1,1,1-CH 3 CCl 3 ) Terrestrial e
TABLE 8.7 (w) Ammonia (NH 4 + , NH 3 , as N) (r) Zinc (Zn, ore) (r) Oil (in ground) (r) Natural gas (in ground) (r) Phosphate rock (in ground) Air acidification (g equiv. H + ) (a) Sulfur oxides (SOx as SO 2 ) (a) Methane (CH 4 ) (w) Cadmium (Cd ++ ) (a) Mercury (Hg) (w) Chromium (Cr III) (w) Ammonia (NH 4 + , NH 3 , as N) (a)