Page 25 - Intelligent Communication Systems
P. 25
CHAPTER 2 / COMMUNICATION FUNDAMENTALS 9
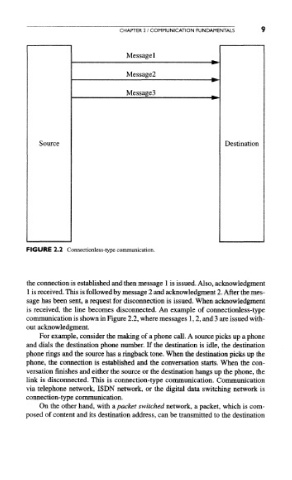
FIGURE 2.2 Connectionless-type communication.
the connection is established and then message 1 is issued. Also, acknowledgment
1 is received. This is followed by message 2 and acknowledgment 2. After the mes-
sage has been sent, a request for disconnection is issued. When acknowledgment
is received, the line becomes disconnected. An example of connectionless-type
communication is shown in Figure 2.2, where messages 1,2, and 3 are issued with-
out acknowledgment.
For example, consider the making of a phone call. A source picks up a phone
and dials the destination phone number. If the destination is idle, the destination
phone rings and the source has a ringback tone. When the destination picks up the
phone, the connection is established and the conversation starts. When the con-
versation finishes and either the source or the destination hangs up the phone, the
link is disconnected. This is connection-type communication. Communication
via telephone network, ISDN network, or the digital data switching network is
connection-type communication.
On the other hand, with a packet switched network, a packet, which is com-
posed of content and its destination address, can be transmitted to the destination